 TensorFlow 1 version
TensorFlow 1 version
|
Partitions data into num_partitions tensors using indices from partitions.
tf.dynamic_partition(
data, partitions, num_partitions, name=None
)
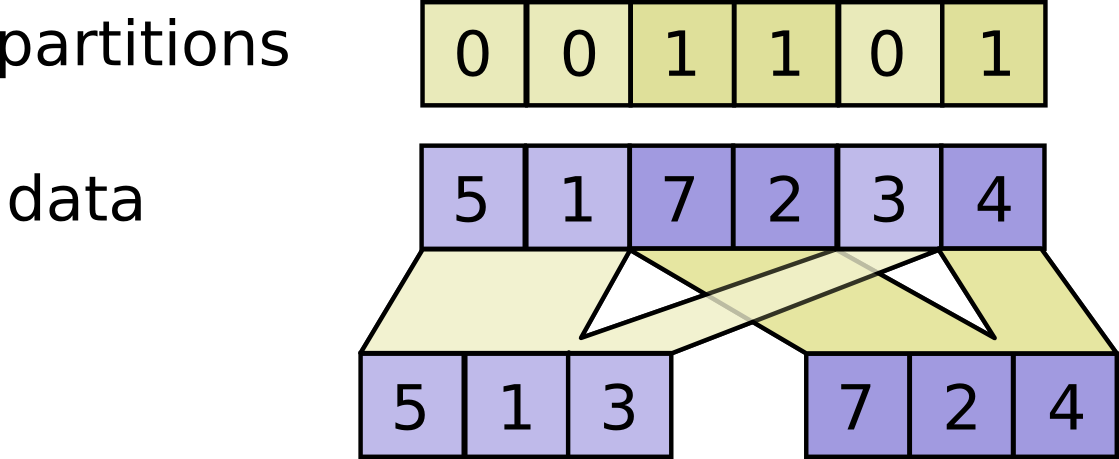
For each index tuple js of size partitions.ndim, the slice data[js, ...]
becomes part of outputs[partitions[js]]. The slices with partitions[js] = i
are placed in outputs[i] in lexicographic order of js, and the first
dimension of outputs[i] is the number of entries in partitions equal to i.
In detail,
outputs[i].shape = [sum(partitions == i)] + data.shape[partitions.ndim:]
outputs[i] = pack([data[js, ...] for js if partitions[js] == i])
data.shape must start with partitions.shape.
For example:
# Scalar partitions.
partitions = 1
num_partitions = 2
data = [10, 20]
outputs[0] = [] # Empty with shape [0, 2]
outputs[1] = [[10, 20]]
# Vector partitions.
partitions = [0, 0, 1, 1, 0]
num_partitions = 2
data = [10, 20, 30, 40, 50]
outputs[0] = [10, 20, 50]
outputs[1] = [30, 40]
See dynamic_stitch for an example on how to merge partitions back.
Args | |
|---|---|
data
|
A Tensor.
|
partitions
|
A Tensor of type int32.
Any shape. Indices in the range [0, num_partitions).
|
num_partitions
|
An int that is >= 1.
The number of partitions to output.
|
name
|
A name for the operation (optional). |
Returns | |
|---|---|
A list of num_partitions Tensor objects with the same type as data.
|
