0% found this document useful (0 votes)
2K views23 pagesBrand Decision-Making Guide
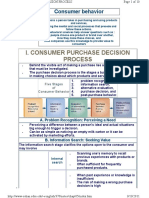
The document discusses the brand decision process and how brands must speak to both rational and emotional aspects. It outlines 3 factors that influence decisions: involvement level, customers vs prospects, and consumers vs businesses. Brand decision-making exists on a head-to-heart continuum. There are 3 approaches: cognitive, affective, and combined. Decision-making is also related to involvement level. The 5 basic decision-making steps are: problem recognition, information search, choice evaluation, action, and review. Brand messages must get attention and be relevant during information search. Risks are evaluated in choice evaluation. Attitudes and behaviors are linked but not always direct. Learning occurs from the review process. Persuasion models include AIDA and think
Uploaded by
Mudassir KarnolwalCopyright
© Attribution Non-Commercial (BY-NC)
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as PPT, PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd
0% found this document useful (0 votes)
2K views23 pagesBrand Decision-Making Guide
The document discusses the brand decision process and how brands must speak to both rational and emotional aspects. It outlines 3 factors that influence decisions: involvement level, customers vs prospects, and consumers vs businesses. Brand decision-making exists on a head-to-heart continuum. There are 3 approaches: cognitive, affective, and combined. Decision-making is also related to involvement level. The 5 basic decision-making steps are: problem recognition, information search, choice evaluation, action, and review. Brand messages must get attention and be relevant during information search. Risks are evaluated in choice evaluation. Attitudes and behaviors are linked but not always direct. Learning occurs from the review process. Persuasion models include AIDA and think
Uploaded by
Mudassir KarnolwalCopyright
© Attribution Non-Commercial (BY-NC)
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as PPT, PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd
/ 23