0% found this document useful (0 votes)
315 views4 pagesPOM All Formulas
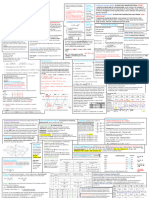
The document discusses various operations management concepts and formulas related to productivity, plant location analysis, break even analysis, cycle time, efficiency, forecasting, regression, demand elasticity, capacity utilization, project scheduling, inventory management, and economic order quantity. Key concepts include outputs over inputs for productivity, weighted score and centroid methods for plant location, comparing total costs of locations in break even analysis, relating production time and required outputs for cycle time, comparing actual to theoretical cycles for efficiency, and formulas for forecasting errors, regression, demand and price elasticities, expected times, and inventory carrying costs.
Uploaded by
Bhawin DondaCopyright
© Attribution Non-Commercial (BY-NC)
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as DOC, PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd
0% found this document useful (0 votes)
315 views4 pagesPOM All Formulas
The document discusses various operations management concepts and formulas related to productivity, plant location analysis, break even analysis, cycle time, efficiency, forecasting, regression, demand elasticity, capacity utilization, project scheduling, inventory management, and economic order quantity. Key concepts include outputs over inputs for productivity, weighted score and centroid methods for plant location, comparing total costs of locations in break even analysis, relating production time and required outputs for cycle time, comparing actual to theoretical cycles for efficiency, and formulas for forecasting errors, regression, demand and price elasticities, expected times, and inventory carrying costs.
Uploaded by
Bhawin DondaCopyright
© Attribution Non-Commercial (BY-NC)
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as DOC, PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd
/ 4