Chapter 1
INTRODUCTION
TO
EMBEDDED SYSTEM
Mr. Azhar Bin Jaffar
Lecturer
Electrical Engineering Department
Politeknik Ungku Omar
�Discussion
What are some components of a
computer?
What is a Microprocessor?
A Microcontroller?
An Embedded System?
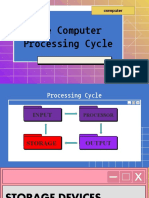
�Components of a Computer
Central Processing Unit
Interprets and carries out all the instructions
contained in software
Memory
Used to store instructions and data
Random Access Memory (RAM)
Read Only Memory (ROM)
Input/Output
Used to communicate with the outside world
�Block diagram of a computer system
a)
b)
c)
d)
e)
Central processing unit (CPU)
Main memory
Secondary memory
Input unit
Output unit
�Microprocessor
A single chip that contains a whole CPU
Has the ability to fetch and execute
instructions stored in memory
Has the ability to access external memory,
external I/O and other peripherals
Examples:
Intel P4 or AMD Athlon in
desktops/notebooks
ARM processor in Apple iPod
�Microcontroller
Essentially a microprocessor with on-chip memories
and I/O devices
Designed for specific functions
All in one solution - Reduction in chip count
Reduced cost, power, physical size, etc.
Examples
PIC16F877A, MC68332, MC68HC11, PPC555
More details of components
A/D and D/A converters, PWM, communications,
timing circuits, many others
�Microcontroller and its component
�Microprocessor in a Microcontroller
�Micro P VS Micro C
Microprocessor-based System
A/D
Analog
I/O
Input
and
output
ports
EEPROM
Microprocessor
ROM
RAM
Serial I/O
Input
and
output
ports
Parallel I/O
Timer
D/A
PWM
Microcontroller-based System
�Micro P VS Micro C
The microprocessor is a processor
on one silicon chip.
The microcontrollers are used in
embedded computing.
The microcontroller is a
microprocessor with added circuitry.
�1.1 What Is an Embedded System?
An embedded system is a special-purpose
computer system designed to perform one or a few
dedicated functions, often with real-time computing
constraints.
It is usually embedded as part of a complete device
including hardware and mechanical parts.
In contrast, a general-purpose computer, such as a
personal computer, can do many different tasks
depending on programming.
Embedded systems control many of the common
devices in use today.
-- Wikipedia
�Definition
Hard to define
Computing systems embedded within
electronic devices
Nearly any computing system other
than a desktop computer
��Embedded System Application
�Microcontroller in a car
��Car Electronic System
�Embedded System Example
Automotive:
Ignition System
Engine Control
ABS
Air Bag
Instrumentation
Security System
Transmission
Control
Entertainment
Climate Control
Cellular Phone
Keyless Entry
Home
Automation:
Office
Automation:
Fax Machine
Laser Printers
Color Printer
Scanners
Paging
Copier
Air conditioner
Industrial
Control:
Robotics and Control Systems
Appliances
Intercom
Telephones
Security Systems
TVs
Cable TV Tuner
Camcorder
DVD Player
Remote control
Video Games
Lighting Control
Toys
Sewing Machines
�Common Characteristics of Embedded Systems
Single-functioned
Executes a single program, repeatedly.
Tightly-constrained
Low cost, low power, small, fast, etc.
Reactive and real-time
Continually reacts to changes in the systems environment.
Must compute certain results in real-time without delay
�Advantages of Microcontroller
Application
Design and Efficiency
The central processing core in embedded systems is generally
less complicated, making it easier to maintain.
The limited function required of embedded systems allows them
to be designed to most efficiently perform their functions.
Cost
The streamlined make-up of most embedded systems allows
their parts to be smaller less expensive to produce.
�Advantages of Microcontroller
Application
Accessibility
Embedded systems are difficult to service because they are
inside another machine, so a greater effort is made to carefully
develop them.
This concern is sometimes addressed in the design stage, such
as by programming an embedded system so that it will not affect
related systems negatively when malfunctioning.
Maintenance
Embedded systems are easier to maintain because the supplied
power is embedded in the system and does not require remote
maintenance.
Redundancies
Embedded systems do not involve the redundant programming
and maintenance involved in other system models.
�Advantages of Microcontroller
Application
Replacement of discrete logic-based circuits.
Provide functional upgrades.
Improve mechanical performance.
Replacement of analog circuits.