0% found this document useful (0 votes)
94 views21 pagesMicro-Controller: Emergers Technologies
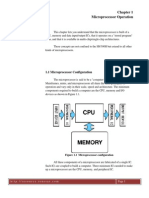
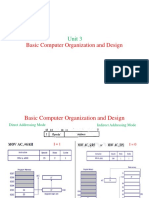
A micro-controller contains a CPU, RAM, ROM, I/O ports and other components on a single chip to control electronic devices. A microprocessor only contains a CPU and requires external components. Micro-controllers are application specific, have more hardware and are cheaper to produce while microprocessors are general purpose, have less hardware and are more expensive to produce. Common examples of micro-controllers include 8051 and PIC while microprocessors include 8085 and ARM.
Uploaded by
prajun_kumar3Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd
0% found this document useful (0 votes)
94 views21 pagesMicro-Controller: Emergers Technologies
A micro-controller contains a CPU, RAM, ROM, I/O ports and other components on a single chip to control electronic devices. A microprocessor only contains a CPU and requires external components. Micro-controllers are application specific, have more hardware and are cheaper to produce while microprocessors are general purpose, have less hardware and are more expensive to produce. Common examples of micro-controllers include 8051 and PIC while microprocessors include 8085 and ARM.
Uploaded by
prajun_kumar3Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd
/ 21