1 Installation Planning
SAP AG
1.2 Distribution of Components to Disks
For a distribution that is suitable for a small test or demo system, see the example Minimal
Configuration [page 22].
List of required file systems
Refer to SAP File Systems [page 23] and Oracle File Systems [page 26] to get the minimum file
system sizes required for the installation.
1.2.1 Recommended Configuration
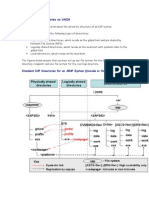
The following diagram shows an optimal distribution of the database data on different disks.
Backup of
log files
Redo
Logs
Set A
DB data
Redo
Logs
Set B
Mirrored
Redo
Logs
Set A
Mirrored
Redo
Logs
Set B
Optimal Distribution
1.2.2 Minimal Configuration
This configuration should only be used for test or demo systems.
Device 1: Backup of redo logs
Device 2: Redo logs and database data
Device 3: Mirrored redo logs and database data
22
July 2000
�SAP AG
1 Installation Planning
1.2 Distribution of Components to Disks
Backup of
log files
Redo
logs
Mirrored
Redo logs
DB data
DB data
Minimal Configuration
Although this "minimal configuration" satisfies the SAP security requirements, it has the following
disadvantages:
Security
The minimal configuration does not ensure that both the database files and redo log files
will not be lost if there is a single disk failure.
The minimal configuration makes sure that no data will be lost, but recovery will be
complicated and time-consuming.
Performance
The I/O-intensive redo logs are on the same disk volumes as the data files.
This configuration should only be used at small installations.
1.2.3 SAP File Systems
Definition
You need to set up file systems for the SAP System before the installation. The file systems are
global, that is, they are accessed by all hosts in the SAP System.
File System Name
Description
<sapmnt>/<SAPSID>
Software and data for one SAP
System
Space Required
Central instance and
standalone gateway: 300 MB
Dialog instance (same
platform as central instance):
no file system necessary
Dialog instance (different
platform): 240 MB
/usr/sap/<SAPSID>
Instance-specific data, symbolic
links to the data for one system
Dialog instance with sapcpe
in use: 380 MB
Other instances: 350 MB
/usr/sap/trans
Global transport directory for all
SAP Systems
<db home>
Database home directory
July 2000
100 MB for each SAP instance
Database-specific
23
�1 Installation Planning
SAP AG
1.2 Distribution of Components to Disks
The listed file system sizes are SAP requirements. Depending on your operating
system, you might have to add space for administrative purposes.
The following graphic shows the standard SAP directory structure:
/
usr
sap
<SAPSID>
<SAPSID>
SYS
exe
profile
trans
<Instance name>
global
log
data
work
dbg opt run
<sapmnt>
<SAPSID>
<name>
exe profile global
File system
you have to
set up
manually
Symbolic link
Standard SAP Directory Structure
Use
Directory /<sapmnt>/<SAPSID>
This directory is physically located on the central instance. In homogeneous systems, you need
to mount it by Network File System (NFS) for all hosts belonging to the same SAP System. It
contains the following sub-directories:
exe, containing executable kernel programs
global, containing log files
profile, containing the start and operations profiles of all instances
24
July 2000
�SAP AG
1 Installation Planning
1.2 Distribution of Components to Disks
Directory /usr/sap/<SAPSID>
This directory contains files for the operation of a local instance. There is a sub-directory
<INSTANCE> for each instance installed on the local instance host, whereas data used by
several instances is located in the directory SYS. There are sub-directories of
/usr/sap/<SAPSID>/SYS with symbolic links to sub-directories of /<sapmnt>/<SAPSID>.
R3SETUP sets up these directory structures during the installation.
Since SAP traces for the instance are created in the directory
/usr/sap/<SAPSID>/<INSTANCE>, sufficient space must be available in this
directory. Changes in SAP System profiles can also affect the disk space.
Directory /usr/sap/trans
In an SAP network there must be a global directory, called /usr/sap/trans, for the transport
of objects between SAP Systems. This directory is created on one SAP instance host in the SAP
network (the transport host). It must be accessible by every host on which an SAP instance is
installed and which belongs to this SAP network. The path on every host must be
/usr/sap/trans.
If you want to use the Change and Transport system, additional space is required in directory
/usr/sap/trans. Since the required storage size differs depending on the transport volume,
SAP cannot specify the required amount of free disk space. We recommend that you reserve 20
MB per user of the transport system, with a minimum of 200 MB.
The directory /usr/sap/trans can be a soft link pointing to the transport directory, or it can be
mounted using Network File System (NFS). It should be exported in read/write mode on the
transport host with NFS and mounted on all central and dialog instance hosts.
For more information, see Mounting Directories via NFS [page 217].
July 2000
25
�1 Installation Planning
SAP AG
1.2 Distribution of Components to Disks
1.2.4 Oracle File Systems
The following table gives an overview of the file systems required for the Oracle database. For a
description of the file systems that are required for the SAP System see SAP File Systems [page
23].
File systems required for the Oracle database
File System Name
Oracle 8.0.5, Oracle 8.0.6:
/oracle/<SAPSID>
Oracle 8.1.6:
/oracle/<SAPSID>/816_32 or
/oracle/<SAPSID>/816_64
/oracle/805_32 or
/oracle/805_64
Description
Home directory for Oracle
instance <SAPSID>
($ORACLE_HOME)
Space Required
Central instance with DB: 950 MB
Central or dialog instance: 140 MB
Standalone DB: 950 MB
Directory for Oracle client
software.
20 MB
The directory has to be
named 805_<xy> even if
you are using Oracle 8.0.6
or Oracle 8.1.6.
Oracle 8.0.5:
/oracle/stage/stage_805
Oracle 8.0.6:
/oracle/stage/stage_806
Installation and upgrade
directory for database
software (staging area)
AIX: 600 MB
Compaq Tru64 UNIX: 680 MB
HP-UX, Linux: 500 MB
ReliantUNIX, Solaris: 650 MB
Oracle 8.1.6:
/oracle/stage/816_32 or
/oracle/stage/816_64
/oracle/<SAPSID>/origlogA
Original set A of redo logs
55 MB
/oracle/<SAPSID>/origlogB
Original set B of redo logs
45 MB
/oracle/<SAPSID>/mirrlogA
Mirrored set A of redo logs
55 MB
/oracle/<SAPSID>/mirrlogB
Mirrored set B of redo logs
45 MB
/oracle/<SAPSID>/saparch
Backup of redo logs
350 MB
/oracle/<SAPSID>/sapreorg
Work directory for
database administration
1400 MB
/oracle/<SAPSID>/sapdata1
SAP data
/oracle/<SAPSID>/sapdata2
SAP data
Approximately 8 GB of space are
required for all SAP data files.
/oracle/<SAPSID>/sapdata3
SAP data
/oracle/<SAPSID>/sapdata4
SAP data
/oracle/<SAPSID>/sapdata5
SAP data
/oracle/<SAPSID>/sapdata6
SAP data
26
See SAP Note 311308 for exact
space requirements of each
sapdata file system.
July 2000
�SAP AG
1 Installation Planning
1.2 Distribution of Components to Disks
The file system $ORACLE_HOME (/oracle/<SAPSID>, Oracle 8.1.6:
/oracle/<SAPSID>/816_32 or /oracle/<SAPSID>/816_64) must reside on
a local disk. It cannot be a softlink.
The file system
/oracle/stage/stage_805 (Oracle 8.0.5)
/oracle/stage/stage_806 (Oracle 8.0.6)
/oracle/stage/816_32 (32-bit Oracle 8.1.6)
/oracle/stage/816_64 (64-bit Oracle 8.1.6)
is also used for Oracle upgrades and should not be deleted after the installation.
During system operation, the database writes temporary files to the /oracle/<SAPSID>
directory. SAP therefore reserves more space during installation than the Oracle software needs.
The archive directory /oracle/<SAPSID>/saparch should provide enough space for archives
between two backups. In a production system, between 300 MB and 1 GB data is archived daily.
The listed file system sizes are SAP requirements. Depending on your operating
system, you might have to add space for administrative purposes.
July 2000
27