100% found this document useful (9 votes)
3K views40 pagesMysql Replication & Cluster
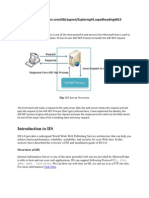
MySQL replication allows data to be replicated from a master database to slave databases, providing scalability and high availability. It works by logging database changes on the master and propagating those changes to slaves. This allows queries to be balanced across slaves for scalability and for a slave to take over if the master fails, improving availability. MySQL cluster provides an alternative clustering method using an in-memory storage engine to share data across nodes, allowing data to be accessed on any node.
Uploaded by
taejunCopyright
© Attribution Non-Commercial (BY-NC)
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd
100% found this document useful (9 votes)
3K views40 pagesMysql Replication & Cluster
MySQL replication allows data to be replicated from a master database to slave databases, providing scalability and high availability. It works by logging database changes on the master and propagating those changes to slaves. This allows queries to be balanced across slaves for scalability and for a slave to take over if the master fails, improving availability. MySQL cluster provides an alternative clustering method using an in-memory storage engine to share data across nodes, allowing data to be accessed on any node.
Uploaded by
taejunCopyright
© Attribution Non-Commercial (BY-NC)
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd
/ 40