0% found this document useful (0 votes)
159 views7 pagesPaki-Rephrase. Ayusin Ang Pagkakasunudsunod. Wag Chorvahin, Gawin!!!trabaho, Trabaho
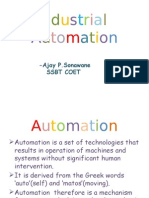
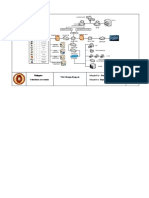
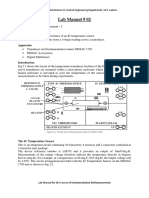
The document discusses automation and programmable logic controllers (PLCs). It defines automation as using control systems and information technology to control industrial machinery and processes, reducing human intervention. PLCs are specialized computers frequently used in automation to synchronize sensor inputs and outputs to devices. The document also discusses mechanization, which uses machinery to assist humans, as compared to automation which greatly reduces human involvement.
Uploaded by
pamplaCopyright
© Attribution Non-Commercial (BY-NC)
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd
0% found this document useful (0 votes)
159 views7 pagesPaki-Rephrase. Ayusin Ang Pagkakasunudsunod. Wag Chorvahin, Gawin!!!trabaho, Trabaho
The document discusses automation and programmable logic controllers (PLCs). It defines automation as using control systems and information technology to control industrial machinery and processes, reducing human intervention. PLCs are specialized computers frequently used in automation to synchronize sensor inputs and outputs to devices. The document also discusses mechanization, which uses machinery to assist humans, as compared to automation which greatly reduces human involvement.
Uploaded by
pamplaCopyright
© Attribution Non-Commercial (BY-NC)
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd
/ 7