0% found this document useful (0 votes)
338 views5 pagesHyperbolic Function
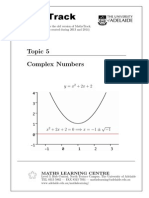
This document discusses hyperbolic functions, including their definitions, graphs, identities, and properties. Some key points:
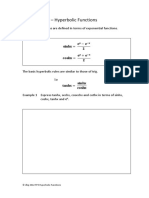
- The hyperbolic sine and cosine functions are defined similarly to trigonometric sine and cosine, but use exponentials instead of trigonometric functions.
- Graphs of common hyperbolic functions like sinh(x), cosh(x), and tanh(x) are presented.
- Several identities involving hyperbolic functions are proved, such as cosh^2(x) - sinh^2(x) = 1.
- Inverse hyperbolic functions like sinh^(-1)(x) are defined and converted to logarithmic form.
- Derivatives
Uploaded by
Saimo MghaseCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as DOC, PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd
0% found this document useful (0 votes)
338 views5 pagesHyperbolic Function
This document discusses hyperbolic functions, including their definitions, graphs, identities, and properties. Some key points:
- The hyperbolic sine and cosine functions are defined similarly to trigonometric sine and cosine, but use exponentials instead of trigonometric functions.
- Graphs of common hyperbolic functions like sinh(x), cosh(x), and tanh(x) are presented.
- Several identities involving hyperbolic functions are proved, such as cosh^2(x) - sinh^2(x) = 1.
- Inverse hyperbolic functions like sinh^(-1)(x) are defined and converted to logarithmic form.
- Derivatives
Uploaded by
Saimo MghaseCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as DOC, PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd
/ 5