0% found this document useful (0 votes)
90 views24 pagesProject Integration & Scope Mgmt
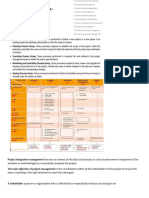
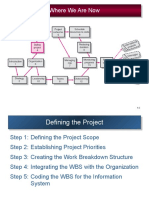
This document discusses project integration and scope management topics for an engineering project management course. It covers developing a project charter and scope statement, work breakdown structures, responsibility matrices, and project evaluation and selection methods. The key learning objectives are to analyze problems during project execution, establish an engineering project's scope and develop a work breakdown structure, and determine if the scope has changed and how to accommodate changes.
Uploaded by
JohnCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd
0% found this document useful (0 votes)
90 views24 pagesProject Integration & Scope Mgmt
This document discusses project integration and scope management topics for an engineering project management course. It covers developing a project charter and scope statement, work breakdown structures, responsibility matrices, and project evaluation and selection methods. The key learning objectives are to analyze problems during project execution, establish an engineering project's scope and develop a work breakdown structure, and determine if the scope has changed and how to accommodate changes.
Uploaded by
JohnCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd
/ 24