SQL General Data Types
Each column in a database table is required to have a name and a data type.
SQL developers have to decide what types of data will be stored inside each and
every table column when creating a SQL table. The data type is a label and a
guideline for SQL to understand what type of data is expected inside of each column,
and it also identifies how SQL will interact with the stored data.
The following table lists the general data types in SQL:
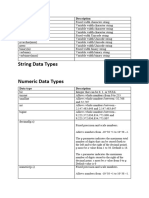
Data type
Description
CHARACTER(n)
Character string. Fixed-length n
VARCHAR(n) or
CHARACTER VARYING(n)
Character string. Variable length. Maximum length n
BINARY(n)
Binary string. Fixed-length n
BOOLEAN
Stores TRUE or FALSE values
VARBINARY(n) or
BINARY VARYING(n)
Binary string. Variable length. Maximum length n
INTEGER(p)
Integer numerical (no decimal). Precision p
SMALLINT
Integer numerical (no decimal). Precision 5
INTEGER
Integer numerical (no decimal). Precision 10
BIGINT
Integer numerical (no decimal). Precision 19
DECIMAL(p,s)
Exact numerical, precision p, scale s. Example: decimal(5,2) is a numb
digits before the decimal and 2 digits after the decimal
NUMERIC(p,s)
Exact numerical, precision p, scale s. (Same as DECIMAL)
FLOAT(p)
Approximate numerical, mantissa precision p. A floating number in bas
exponential notation. The size argument for this type consists of a sing
specifying the minimum precision
REAL
Approximate numerical, mantissa precision 7
FLOAT
Approximate numerical, mantissa precision 16
DOUBLE PRECISION
Approximate numerical, mantissa precision 16
DATE
Stores year, month, and day values
TIME
Stores hour, minute, and second values
TIMESTAMP
Stores year, month, day, hour, minute, and second values
�INTERVAL
Composed of a number of integer fields, representing a period of time,
the type of interval
ARRAY
A set-length and ordered collection of elements
MULTISET
A variable-length and unordered collection of elements
XML
Stores XML data
SQL Data Type Quick Reference
However, different databases offer different choices for the data type definition.
The following table shows some of the common names of data types between the
various database platforms:
Data type
Access
SQLServer
Oracle
MySQL
boolean
Yes/No
Bit
Byte
N/A
integer
Number (integer)
Int
Number
Int
Integer
float
Number (single)
Float
Real
Number
Float
currency
Currency
Money
N/A
N/A
string (fixed)
N/A
Char
Char
Char
string (variable)
Text (<256)
Memo (65k+)
Varchar
Varchar
Varchar2
Varchar
binary object
OLE Object Memo
Binary (fixed up to 8K)
Varbinary (<8K)
Image (<2GB)
Long
Raw
Blob
Text