0% found this document useful (0 votes)
43 views8 pagesMechanics of Materials II:: Thin-Walled Pressure Vessels and Torsion
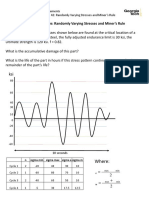
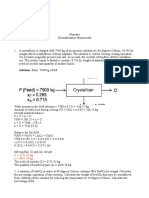
The document discusses mechanics of materials topics including thin-walled pressure vessels, torsional shearing stress and strain, and elastic and inelastic torsion of straight cylindrical shafts. It provides formulas for elastic torsion, relates applied torque to stresses and geometry, and develops the relationship used in analyzing inelastic torsion of straight cylindrical shafts. The learning outcome is to understand how to analyze and design for inelastic torsion of straight cylindrical shafts.
Uploaded by
Wolf LordCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd
0% found this document useful (0 votes)
43 views8 pagesMechanics of Materials II:: Thin-Walled Pressure Vessels and Torsion
The document discusses mechanics of materials topics including thin-walled pressure vessels, torsional shearing stress and strain, and elastic and inelastic torsion of straight cylindrical shafts. It provides formulas for elastic torsion, relates applied torque to stresses and geometry, and develops the relationship used in analyzing inelastic torsion of straight cylindrical shafts. The learning outcome is to understand how to analyze and design for inelastic torsion of straight cylindrical shafts.
Uploaded by
Wolf LordCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd
/ 8