100% found this document useful (1 vote)
5K views4 pagesAPI Thread Measurement PDF
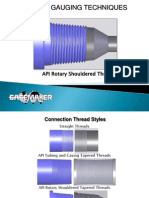
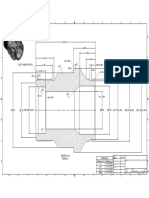
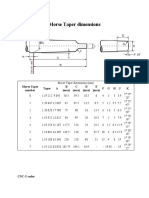
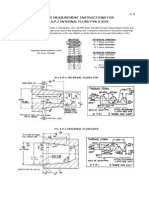
This document provides instructions for measuring API thread dimensions using thread inserts and a digital caliper. It defines key thread parameters like major diameter, pitch diameter, and flank angle. It explains that API threads typically have tapers of 1 1/4, 1 1/2, 2, or 3 inches per foot. The instructions describe how to properly zero the caliper, position the inserts at the correct distance from the shoulder, and calculate additions or subtractions to the measurement to account for taper. Calibration plates and plug/ring gages are recommended to verify accurate measurements.
Uploaded by
DarkedgeCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd
100% found this document useful (1 vote)
5K views4 pagesAPI Thread Measurement PDF
This document provides instructions for measuring API thread dimensions using thread inserts and a digital caliper. It defines key thread parameters like major diameter, pitch diameter, and flank angle. It explains that API threads typically have tapers of 1 1/4, 1 1/2, 2, or 3 inches per foot. The instructions describe how to properly zero the caliper, position the inserts at the correct distance from the shoulder, and calculate additions or subtractions to the measurement to account for taper. Calibration plates and plug/ring gages are recommended to verify accurate measurements.
Uploaded by
DarkedgeCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd
/ 4