0% found this document useful (0 votes)
2K views5 pagesFundamentals of Computer Security
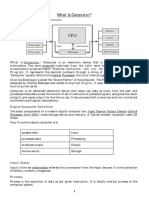
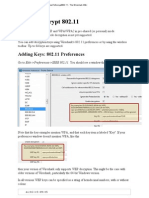
Computer security refers to protecting computer systems and data from threats. It aims to maintain confidentiality, integrity, and availability. Key elements include threats, exploits, vulnerabilities, attacks, and data theft. Computer security is important due to increasing system complexity, easier exploits, and more network access points. Maintaining security requires precautions, updates, and timely responses. Layers include physical, network, system, application, and user security. Computer security awareness helps minimize attacks and information loss.
Uploaded by
Rosen LPCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd
0% found this document useful (0 votes)
2K views5 pagesFundamentals of Computer Security
Computer security refers to protecting computer systems and data from threats. It aims to maintain confidentiality, integrity, and availability. Key elements include threats, exploits, vulnerabilities, attacks, and data theft. Computer security is important due to increasing system complexity, easier exploits, and more network access points. Maintaining security requires precautions, updates, and timely responses. Layers include physical, network, system, application, and user security. Computer security awareness helps minimize attacks and information loss.
Uploaded by
Rosen LPCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd
/ 5