0% found this document useful (0 votes)
60 views7 pagesProgram To Create A Linked List22
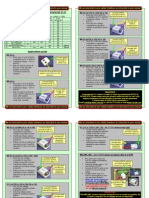
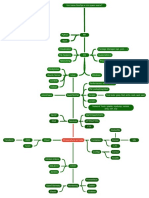
The document discusses creating and manipulating linked lists in C/C++. It includes functions to:
1) Add nodes to the front (push), back (append), and middle (insertAfter) of linked lists.
2) Print the contents of a linked list by traversing from the head node to the tail node.
3) A main function demonstrates using these functions to build a sample linked list and print it.
Uploaded by
ĨnÔøcềnt PrîñçêCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd
0% found this document useful (0 votes)
60 views7 pagesProgram To Create A Linked List22
The document discusses creating and manipulating linked lists in C/C++. It includes functions to:
1) Add nodes to the front (push), back (append), and middle (insertAfter) of linked lists.
2) Print the contents of a linked list by traversing from the head node to the tail node.
3) A main function demonstrates using these functions to build a sample linked list and print it.
Uploaded by
ĨnÔøcềnt PrîñçêCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd
/ 7