0% found this document useful (0 votes)
195 views4 pagesChapter: 7.2 Database Topic: 7.2.1 Introduction To Database: E-Content of It Tools and Business System
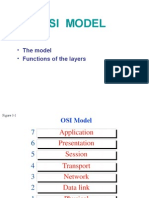
This document discusses databases and database management systems. It defines data as isolated facts with implicit meaning. A database is an organized collection of related data that allows users to efficiently retrieve desired information. A database management system (DBMS) is a set of programs used to create and maintain a database, allowing users to add, update and delete data. Relational databases organize data into tables with rows and columns, and allow querying and reassembling of data in different ways through relationships between tables.
Uploaded by
ETL LABSCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd
0% found this document useful (0 votes)
195 views4 pagesChapter: 7.2 Database Topic: 7.2.1 Introduction To Database: E-Content of It Tools and Business System
This document discusses databases and database management systems. It defines data as isolated facts with implicit meaning. A database is an organized collection of related data that allows users to efficiently retrieve desired information. A database management system (DBMS) is a set of programs used to create and maintain a database, allowing users to add, update and delete data. Relational databases organize data into tables with rows and columns, and allow querying and reassembling of data in different ways through relationships between tables.
Uploaded by
ETL LABSCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd
/ 4