0% found this document useful (0 votes)
201 views3 pagesThere Are 3 Key Elements To A Contactor
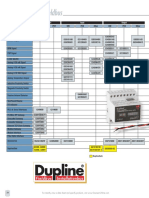
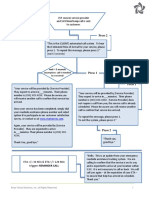
There are 3 key elements to selecting a contactor: main contacts, auxiliary contacts, and coil. The main criteria for selection include the number of contacts, current and voltage ratings, duty, and load details. Auxiliary contact criteria include the number required and signaling application details. Coil criteria include the voltage rating, whether AC or DC, frequency for AC coils, and low power requirements if applicable. Additional information like enclosure type, design requirements, operations per hour, latching operation, environment, and ancillary components should also be provided.
Uploaded by
Sharath KotaCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd
0% found this document useful (0 votes)
201 views3 pagesThere Are 3 Key Elements To A Contactor
There are 3 key elements to selecting a contactor: main contacts, auxiliary contacts, and coil. The main criteria for selection include the number of contacts, current and voltage ratings, duty, and load details. Auxiliary contact criteria include the number required and signaling application details. Coil criteria include the voltage rating, whether AC or DC, frequency for AC coils, and low power requirements if applicable. Additional information like enclosure type, design requirements, operations per hour, latching operation, environment, and ancillary components should also be provided.
Uploaded by
Sharath KotaCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd
/ 3