0% found this document useful (0 votes)
83 views13 pagesStructures C Programming: What Is Structure and Its Need?
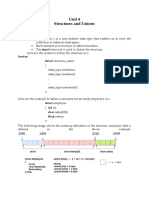
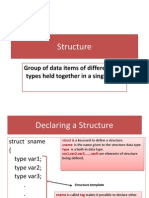
The document discusses structures in C programming. It explains that a structure allows grouping of related data types under one name. It provides an example of defining a structure to store information about a person like name, citizenship number, and salary. It also discusses creating structure variables, accessing structure members, passing structures as function arguments, returning structures from functions, nested structures, and arrays of structures.
Uploaded by
Neha RajuCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd
0% found this document useful (0 votes)
83 views13 pagesStructures C Programming: What Is Structure and Its Need?
The document discusses structures in C programming. It explains that a structure allows grouping of related data types under one name. It provides an example of defining a structure to store information about a person like name, citizenship number, and salary. It also discusses creating structure variables, accessing structure members, passing structures as function arguments, returning structures from functions, nested structures, and arrays of structures.
Uploaded by
Neha RajuCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd
/ 13