0% found this document useful (0 votes)
269 views19 pagesELEX Formula
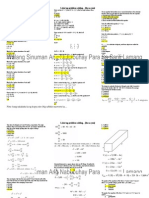
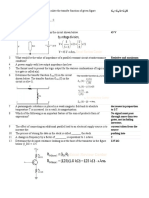
This document provides an overview of topics in power electronics and instrumentation. It covers power conditioning circuits like rectifiers and inverters, as well as switched-mode power supplies. Measurement devices like bridges, tachometers and stroboscopes are discussed. Oscillator circuits including phase shift, Wein bridge, and multivibrators are summarized. Finally, the document touches on solid state devices, energy conversion components, and industrial electronics switches.
Uploaded by
SKYE LightsCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd
0% found this document useful (0 votes)
269 views19 pagesELEX Formula
This document provides an overview of topics in power electronics and instrumentation. It covers power conditioning circuits like rectifiers and inverters, as well as switched-mode power supplies. Measurement devices like bridges, tachometers and stroboscopes are discussed. Oscillator circuits including phase shift, Wein bridge, and multivibrators are summarized. Finally, the document touches on solid state devices, energy conversion components, and industrial electronics switches.
Uploaded by
SKYE LightsCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd
/ 19