0% found this document useful (0 votes)
513 views110 pagesInput Output Storage Devices PDF
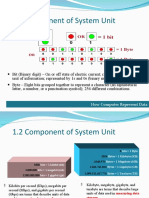
Input devices allow users to enter data and instructions into a computer. Some common input devices include keyboards, pointing devices like mice and touchpads, touch screens, cameras, microphones, and scanners. Storage devices preserve digital data even when the computer is turned off. Output devices display or print the results of processing from the computer.
Uploaded by
Saqib ShaukatCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd
0% found this document useful (0 votes)
513 views110 pagesInput Output Storage Devices PDF
Input devices allow users to enter data and instructions into a computer. Some common input devices include keyboards, pointing devices like mice and touchpads, touch screens, cameras, microphones, and scanners. Storage devices preserve digital data even when the computer is turned off. Output devices display or print the results of processing from the computer.
Uploaded by
Saqib ShaukatCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd
/ 110