100% found this document useful (2 votes)
238 views5 pagesD M A I C Dmaic: Topic 2.1. Definition Phase
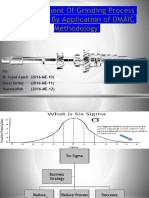
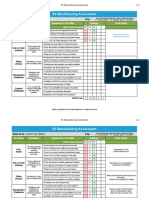
The document describes the DMAIC process used in Six Sigma methodology. DMAIC provides a structure to solve process problems in existing processes. It consists of five phases: Define, Measure, Analyze, Improve, and Control. Each phase has objectives and tools used. The Define phase clarifies the problem and customer requirements. Measure develops measurement systems. Analyze identifies root causes of variation. Improve generates and selects solutions. Control implements solutions and maintains gains.
Uploaded by
Angelica Moscoso Chavez CCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd
100% found this document useful (2 votes)
238 views5 pagesD M A I C Dmaic: Topic 2.1. Definition Phase
The document describes the DMAIC process used in Six Sigma methodology. DMAIC provides a structure to solve process problems in existing processes. It consists of five phases: Define, Measure, Analyze, Improve, and Control. Each phase has objectives and tools used. The Define phase clarifies the problem and customer requirements. Measure develops measurement systems. Analyze identifies root causes of variation. Improve generates and selects solutions. Control implements solutions and maintains gains.
Uploaded by
Angelica Moscoso Chavez CCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd
/ 5