0% found this document useful (0 votes)
36 views32 pagesIntroduction To Databases in Python: Filtering and Targeting Data
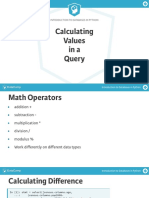
This document provides an introduction to working with databases in Python. It discusses how to filter and target data using where clauses to restrict queries based on conditions. It also covers using expressions, conjunctions, and ordering results. Finally, it discusses counting, summing and grouping data using SQL functions, and connecting the results to Pandas and visualization in Python.
Uploaded by
NourheneMbarekCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd
0% found this document useful (0 votes)
36 views32 pagesIntroduction To Databases in Python: Filtering and Targeting Data
This document provides an introduction to working with databases in Python. It discusses how to filter and target data using where clauses to restrict queries based on conditions. It also covers using expressions, conjunctions, and ordering results. Finally, it discusses counting, summing and grouping data using SQL functions, and connecting the results to Pandas and visualization in Python.
Uploaded by
NourheneMbarekCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd
/ 32