0% found this document useful (0 votes)
225 views8 pagesSwitching and Intelligent Networks
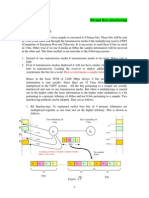
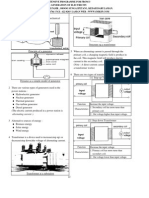
The document introduces intelligent networks, which separate the software controlling basic switch functionality from software controlling call progression. This allows for more advanced features to be rapidly introduced and enables the introduction of advanced customer-oriented services rapidly and cost-effectively. Intelligent networks involve removing service data from switches to a centralized database and separating service logic from switches by placing it in an independent intelligent node called a service control point. This framework provides standardized creation and management of services across multiple vendors.
Uploaded by
Aman KemalCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd
0% found this document useful (0 votes)
225 views8 pagesSwitching and Intelligent Networks
The document introduces intelligent networks, which separate the software controlling basic switch functionality from software controlling call progression. This allows for more advanced features to be rapidly introduced and enables the introduction of advanced customer-oriented services rapidly and cost-effectively. Intelligent networks involve removing service data from switches to a centralized database and separating service logic from switches by placing it in an independent intelligent node called a service control point. This framework provides standardized creation and management of services across multiple vendors.
Uploaded by
Aman KemalCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd
/ 8