100% found this document useful (2 votes)
264 views5 pagesOne Day Seminar: A Report For
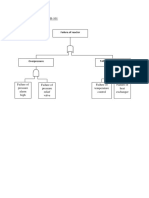
The document discusses process safety management (PSM) in manufacturing industries. PSM involves identifying and controlling process hazards to protect employees, facilities, and the environment. It requires identifying high and low hazard processes, developing a strong safety culture, and implementing 14 key elements of an effective PSM system, including process safety information, hazard analysis, operating procedures, training, and incident investigation. Regular audits and continual improvement are important for an effective PSM system.
Uploaded by
BrijeshCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd
100% found this document useful (2 votes)
264 views5 pagesOne Day Seminar: A Report For
The document discusses process safety management (PSM) in manufacturing industries. PSM involves identifying and controlling process hazards to protect employees, facilities, and the environment. It requires identifying high and low hazard processes, developing a strong safety culture, and implementing 14 key elements of an effective PSM system, including process safety information, hazard analysis, operating procedures, training, and incident investigation. Regular audits and continual improvement are important for an effective PSM system.
Uploaded by
BrijeshCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd
/ 5