Worksheet:
Binary Search Tree
Recap
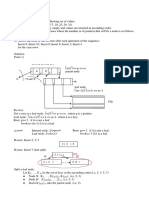
● A binary search tree (BST) is a binary tree where
a. ...the value in each node to its left subtree is less than the current node
b. ...the value in each node to its right subtree is greater than the current node
● The reason why we use BST is so that we can have a data structure where we can search
for values efficiently.
● You can also perform binary search on a sorted array
● Looking up a value takes O(log(n)) if the tree is balanced or O(h) where h is the height of
the tree
Exercise 1
Learn the basics of BSTs
The whole point of BST is to be able to retrieve values quickly. For example, most
implementations of ordered set data structures are actually just binary search trees. Hence know
how to search through a tree is vital for coding interviews. If you mess that up, you might get
automatically rejected. The data structure of a Tree usually looks like this:
# class TreeNode:
# def __init__(self, x):
# self.val = x
# self.left = None
# self.right = None
Solve all the following questions in your preferred language.
1
�
Search in a Binary Search Tree
Given the root node of a binary search tree (BST) and a value. You need to find the node in the
BST that the node's value equals the given value. Return the subtree rooted with that node. If
such node doesn't exist, you should return NULL.
For example,
Example:
Given the tree:
4
/ \
2 6
/ \
1 3
And the value to search: 2
You should return this subtree:
2
/ \
1 3
In the example above, if we want to search the value 5, since there is no node with value 5, we
should return NULL.
Insert into a Binary Search Tree
For example,
Given the tree:
4
/ \
2 7
/ \
1 3
And the value to insert: 5
You can return this binary search tree:
2
�
4
/ \
2 7
/ \ /
1 3 5
This tree is also valid:
5
/ \
2 7
/ \
1 3
\
4
Delete Node in a BST
Example:
root = [5,3,6,2,4,null,7]
key = 3
5
/ \
3 6
/ \ \
2 4 7
Given key to delete is 3. So we find the node with value 3 and delete it.
One valid answer is [5,4,6,2,null,null,7], shown in the following BST.
5
/ \
4 6
/ \
2 7
Another valid answer is [5,2,6,null,4,null,7].
5
/ \
3
�
2 6
\ \
4 7
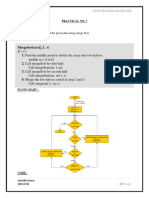
Exercise 2
Applying BST strategies
The following question is a bit more difficult. It requires a bit more creativity, but you have
everything you need to solve it. Try to solve this question using BST and time yourself.
Kth Largest Element in a Stream
Design a class to find the kth largest element in a stream. Note that it is the kth largest element in
the sorted order, not the kth distinct element.
Your KthLargest class will have a constructor which accepts an integer k and an integer array
nums, which contains initial elements from the stream. For each call to the method
KthLargest.add, return the element representing the kth largest element in the stream.
Example:
int k = 3;
int[] arr = [4,5,8,2];
KthLargest kthLargest = new KthLargest(3, arr);
kthLargest.add(3); // returns 4
kthLargest.add(5); // returns 5
kthLargest.add(10); // returns 5
kthLargest.add(9); // returns 8
kthLargest.add(4); // returns 8
Note:
You may assume that nums' length ≥ k-1 and k ≥ 1.
4