0% found this document useful (0 votes)
111 views10 pagesLinear Systems Notes
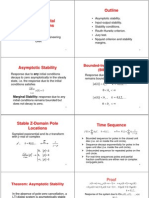
The document discusses linear time-invariant (LTI) discrete systems. It defines LTI systems and explains that the output of an LTI system when excited by an input signal is the convolution of the input signal with the system's impulse response. As an example, it shows how to calculate the impulse response of an LTI system by time-shifting and multiplying the input signal values.
Uploaded by
NicolasHenaoCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd
0% found this document useful (0 votes)
111 views10 pagesLinear Systems Notes
The document discusses linear time-invariant (LTI) discrete systems. It defines LTI systems and explains that the output of an LTI system when excited by an input signal is the convolution of the input signal with the system's impulse response. As an example, it shows how to calculate the impulse response of an LTI system by time-shifting and multiplying the input signal values.
Uploaded by
NicolasHenaoCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd
/ 10