Lecturer: MR.
TSEPISO MOHALE
INTRODUCTION TO COMPUTER SKILLS 2:
CHA P T E R 7/ OPERATING SYSTEMS
In this chapter, will learn:
a) Define the term operating system and discuss major operating system functions.
b) Compare and contrast commonly used operating systems:
• Windows
• Unix/Linux
• Apple
c) Distinguish between system software and application software.
d) Distinguish between a command-based system and graphical user interface.
Demonstrate the following:
e) Discuss popular file types (MS Office, images, PDF, text files) and their
association with software programs
f) Identify and describe the parts and use of a window in a GUI.
g) Distinguish between active window and background items.
h) Demonstrate desktop management skills:
• Use themes, screen savers, backgrounds
• Use Tiling, cascading
• Use Short-cuts and icons
• Use Task bar, Quick Launch, Desktop menus
1
�i) Demonstrate file management skills:
• Create and recognize valid file names and folders
• Use find, copy, move, rename, delete files and folders
• Explain the deletion process and recovery methods
j) Demonstrate how to navigate and select using GUI tools
Use the operating system Help system to find answers to questions about operations and
command usage
OPERATING SYSTEMS
Manages computer hardware and software resources and provides common services for
computer programs. The operating system is a component of the system software in a
computer system. Application programs usually require an operating system to function.
Characteristics of OS:
2
� FUNCTION OF OS
For hardware functions such as input and output and memory allocation, the operating
system acts as an intermediary between programs and the computer hardware, although
the application code is usually executed directly by the hardware and frequently makes
system calls to an OS function or is interrupted by it. Operating systems are found on
many devices that contain a computer – from cellular phones and video game consoles
to web servers and supercomputers.
3
�STARTING THE COMPUTER
4
� EXAMPLES OF OS
Examples of popular desktop operating systems include Apple OS X, Linux and its
variants, and Microsoft Windows. Mobile operating systems include Android,
blackberry OS and iOS among others.
Task 1- Find the meaning of Real Time OS
COMMON OS AND THEIR DIFFERENCES
Windows OS- is an OS most commonly found on personal computers and now
making its way into the mobile and server markets. Windows is developed by
Microsoft and is proprietary commercial software, which has a closed source. That is,
it cannot be modified at its source code for a user’s personal preference.
The latest edition of the Windows OS is the windows 10 operating system.
5
�Apple OS X- OS X is a desktop OS for computers made from manufactured by Apple
Inc. It is closed source and commercial software.
The latest edition of the OS X is the OS X Sierra.
Linux- This is software based on the UNIX family of OS, which are open source and free
to modify. As a result, it has become most popular in servers. It has many variants such
as Ubuntu and red hat, each of which has its own editions.
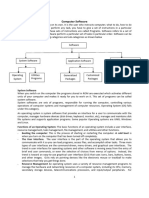
SYSTEM SOFTWARE VERSUS APPLICATION SOFTWARE
HOW DOES THE SOFTWARE WORK?
Software is the computerized instructions that operate the computer, execute
particular functions or tasks, and manipulate the data. For software (the instructions) to
perform various functions, it must be programmed. That is, the instructions need to be
written in a programming language that the computer can understand. Without a
program, a computer is useless.
Programming language: An artificial set of rules, vocabulary and syntax used to
instruct the computer to execute certain tasks.
Computer program: A sequence of instructions that can be executed by a computer
to carry out a process.
There are two types of software
• System Software
• Application Software
6
�System Software
The system software is collection of programs designed to operate, control, and extend
the processing capabilities of the computer itself. System software are generally prepared
by computer manufactures. These software products comprise of programs written in low-
level languages which interact with the hardware at a very basic level. System software
serves as the interface between hardware and the end users.
Systems software includes the operating system and all the utilities that enable the
computer to function. The most important program that runs on a computer is the
operating system. Every general-purpose computer must have an operating system in
order to run other programs. This includes controlling functions such as the coordination
of the hardware and applications software, allocating storage facilities, controlling the
input and output devices and managing time sharing for linked or networked computers.
In many respects an operating system works like an air traffic controller to coordinate
activities within the computer.
Examples of operating systems are Windows NT, DOS and OS/2. The Windows family
of operating systems includes a Graphical User Interface (GUI) that makes the software
user friendly.
Types of system software
• Operating system
• Utility software
Features of system software are as follows:
• Close to system
• Fast in speed
• Difficult to design
• Difficult to understand
• Less interactive
7
�• Smaller in size
• Difficult to manipulate
• Generally written in low-level language
Application Software
Application software products are designed to satisfy a particular need of a particular
environment. All software applications prepared in the computer lab can come under the
category of Application software.
Application software may consist of a single program, such as a Microsoft's notepad for
writing and editing simple text. It may also consist of a collection of programs, often called
a software package, which work together to accomplish a task.
Applications software includes programs that user’s access to carry out work. They
include applications for the following functions:
• Word processing
• Spreadsheets
• Presentation packages and graphics
• Communications applications
Features of application software are as follows:
• Close to user
• Easy to design
• More interactive
• Slow in speed
8
�• Generally written in high-level language
• Easy to understand
• Easy to manipulate and use
• Bigger in size and requires large storage space
System software is a type of computer program that is designed to run a computer's
hardware and application programs while application software help a user to accomplish
a task on the computer.
For example, a computer game is not vital to the operations of the computer and it needs
an OS in order to work, meaning it falls under application software while the OS is system
software.
COMMAND BASED OS SYSTEM VERSUS GRAPHICAL USER INTERFACES
In a command based environment all tasks are achieved through giving commands to a
computer, while in a graphical user interface, menus, graphics and buttons are used to
interact with a computer system.
Command based interface
9
�A graphical User Interface:
Task 1 -for the lecturer- Open a PC and explain the parts of a windows GUI as seen
from the desktop. And explain the difference between active windows and background
items. Explain the Task bar, quick launch and desktop menus.
10
�Utility Programs
Also called utility, is a type of a system software that allows a user to perform maintenance
type task, usually related to managing a computer and its devices, or programs.
Utility Programs are built-in to many operating system or can be purchased separately
Common utility programs includes:
11