0% found this document useful (0 votes)
4 views17 pagesSub ICT Topic 5 - Computer Software
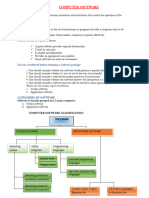
Computer software consists of electronic instructions that guide computers in performing tasks, characterized by traits such as portability, efficiency, and usability. It is classified into system software, which manages hardware and system operations, and application software, which serves specific user needs. Operating systems, a subset of system software, can be categorized based on user support and task execution capabilities, with various types including stand-alone, network, and embedded operating systems.
Uploaded by
kajjjoCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd
0% found this document useful (0 votes)
4 views17 pagesSub ICT Topic 5 - Computer Software
Computer software consists of electronic instructions that guide computers in performing tasks, characterized by traits such as portability, efficiency, and usability. It is classified into system software, which manages hardware and system operations, and application software, which serves specific user needs. Operating systems, a subset of system software, can be categorized based on user support and task execution capabilities, with various types including stand-alone, network, and embedded operating systems.
Uploaded by
kajjjoCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd
/ 17