0% found this document useful (0 votes)
116 views18 pagesADCS Matlab Programs
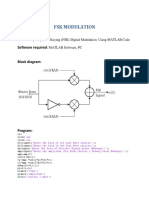
The document describes generating and demodulating frequency shift keying (FSK), quadrature phase shift keying (QPSK), delta modulation, and time division multiplexing signals using MATLAB. It provides the aim, apparatus, procedure, program code, output waveforms, and results for each modulation and demodulation technique. The program code generates the modulated signals, demodulates the signals, and plots the output waveforms such as the modulated signal, demodulated data, and carrier signals.
Uploaded by
surya pratapCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd
0% found this document useful (0 votes)
116 views18 pagesADCS Matlab Programs
The document describes generating and demodulating frequency shift keying (FSK), quadrature phase shift keying (QPSK), delta modulation, and time division multiplexing signals using MATLAB. It provides the aim, apparatus, procedure, program code, output waveforms, and results for each modulation and demodulation technique. The program code generates the modulated signals, demodulates the signals, and plots the output waveforms such as the modulated signal, demodulated data, and carrier signals.
Uploaded by
surya pratapCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd
/ 18