0% found this document useful (0 votes)
200 views16 pagesSection 16.1: Tampilan Table
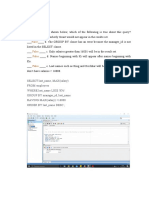
The document discusses creating and managing indexes in Oracle databases. It includes steps to:
1. Create a non-unique index on the cd_number column of the D_TRACK_LISTINGS table.
2. Create a function-based index on the last_name column of the D_PARTNERS table to make searches case-insensitive.
3. Create a synonym for the D_TRACK_LISTINGS table and later drop this synonym.
The document provides explanations of what indexes and ROWIDs are used for in Oracle databases. It also discusses when indexes are automatically created.
Uploaded by
Nabilah AzzahraCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd
0% found this document useful (0 votes)
200 views16 pagesSection 16.1: Tampilan Table
The document discusses creating and managing indexes in Oracle databases. It includes steps to:
1. Create a non-unique index on the cd_number column of the D_TRACK_LISTINGS table.
2. Create a function-based index on the last_name column of the D_PARTNERS table to make searches case-insensitive.
3. Create a synonym for the D_TRACK_LISTINGS table and later drop this synonym.
The document provides explanations of what indexes and ROWIDs are used for in Oracle databases. It also discusses when indexes are automatically created.
Uploaded by
Nabilah AzzahraCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd
/ 16