0% found this document useful (0 votes)
82 views12 pagesStorage Devices Overview
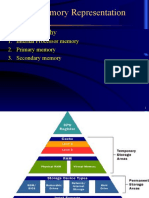
The document compares and contrasts different secondary storage devices, including hard disk drives (HDDs), solid state drives (SSDs), CDs, DVDs, and Blu-Ray discs. HDDs use spinning platters and a moving head to access data, making them slower and more fragile than SSDs, which use flash memory chips. SSDs provide faster read/write speeds, use less battery power, and are more resistant to damage from vibrations or shocks compared to HDDs, but cost more per gigabyte of storage. CDs store the least data while Blu-Ray discs store the most but are also the most expensive format.
Uploaded by
Aryan MaheshwariCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd
0% found this document useful (0 votes)
82 views12 pagesStorage Devices Overview
The document compares and contrasts different secondary storage devices, including hard disk drives (HDDs), solid state drives (SSDs), CDs, DVDs, and Blu-Ray discs. HDDs use spinning platters and a moving head to access data, making them slower and more fragile than SSDs, which use flash memory chips. SSDs provide faster read/write speeds, use less battery power, and are more resistant to damage from vibrations or shocks compared to HDDs, but cost more per gigabyte of storage. CDs store the least data while Blu-Ray discs store the most but are also the most expensive format.
Uploaded by
Aryan MaheshwariCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd
/ 12