100% found this document useful (1 vote)
580 views17 pagesRoad Junctions
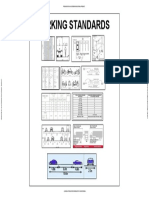
This document discusses different types of road junctions and intersections. It describes traffic islands, which provide safe spaces for pedestrians and divide opposing traffic flows. It then explains four main types of traffic islands: divisional, channelizing, pedestrian loading, and rotary. The document also outlines several types of road junctions and intersections like T-junctions, Y-junctions, staggered junctions, and grade separators. It provides details on different kinds of grade separators like overpasses, underpasses, and several interchange designs like diamond, trumpet, cloverleaf, and Y-type interchanges.
Uploaded by
HarshitBabooCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd
100% found this document useful (1 vote)
580 views17 pagesRoad Junctions
This document discusses different types of road junctions and intersections. It describes traffic islands, which provide safe spaces for pedestrians and divide opposing traffic flows. It then explains four main types of traffic islands: divisional, channelizing, pedestrian loading, and rotary. The document also outlines several types of road junctions and intersections like T-junctions, Y-junctions, staggered junctions, and grade separators. It provides details on different kinds of grade separators like overpasses, underpasses, and several interchange designs like diamond, trumpet, cloverleaf, and Y-type interchanges.
Uploaded by
HarshitBabooCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd
/ 17