0% found this document useful (0 votes)
125 views19 pagesEee1001-Electric Circuits and Systems Lab Assesment
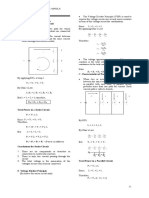
This document contains the lab assessment details of a student. It includes [1] the list of 4 experiments conducted till the mid-exam - verification of Ohm's law, circuit analysis using mesh/nodal analysis, superposition/Thevenin's theorem, and diode characteristics. [2] The circuit diagrams and calculations for experiment 1 verify Ohm's law, voltage and current division rules. [3] Experiment 2 uses mesh/nodal analysis on a given circuit. [4] Experiment 3 applies superposition and Thevenin's theorem on circuits. [5] Experiment 4 analyzes the voltage-current characteristics of a PN junction diode and zener diode.
Uploaded by
Ànuràg Sîngh.Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd
0% found this document useful (0 votes)
125 views19 pagesEee1001-Electric Circuits and Systems Lab Assesment
This document contains the lab assessment details of a student. It includes [1] the list of 4 experiments conducted till the mid-exam - verification of Ohm's law, circuit analysis using mesh/nodal analysis, superposition/Thevenin's theorem, and diode characteristics. [2] The circuit diagrams and calculations for experiment 1 verify Ohm's law, voltage and current division rules. [3] Experiment 2 uses mesh/nodal analysis on a given circuit. [4] Experiment 3 applies superposition and Thevenin's theorem on circuits. [5] Experiment 4 analyzes the voltage-current characteristics of a PN junction diode and zener diode.
Uploaded by
Ànuràg Sîngh.Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd
/ 19