0% found this document useful (0 votes)
34 views25 pages1.2 LS Technological Trends and Implications
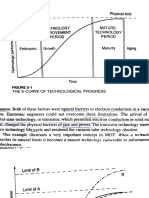
The document discusses technological trends and their implications. It describes the exponential growth of technology and how technological progress follows an S-curve. New technologies can disrupt existing technologies by achieving higher performance through shifting S-curves. The impact of technological change includes shrinking distances, reducing time delays, and enabling virtual simulations. Global trends include globalization, privatization, and constant information flooding.
Uploaded by
Rupak ThapaCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd
0% found this document useful (0 votes)
34 views25 pages1.2 LS Technological Trends and Implications
The document discusses technological trends and their implications. It describes the exponential growth of technology and how technological progress follows an S-curve. New technologies can disrupt existing technologies by achieving higher performance through shifting S-curves. The impact of technological change includes shrinking distances, reducing time delays, and enabling virtual simulations. Global trends include globalization, privatization, and constant information flooding.
Uploaded by
Rupak ThapaCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd
/ 25