0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes) 86 views11 pagesHow JVM Works - JVM Architecture
How JVM Works – JVM Architecture
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content,
claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as PDF or read online on Scribd
oS GeeksforGeeks
Data Structures Algorithms Interview Preparation Topic-wise Practice C++ Java Python
How JVM Works - JVM Architecture?
Difficulty Level: Medium © Last Updated : 15 May, 2021
JVM (Java Virtual Machine) acts as a run-time engine to run Java applications. JVM is
the one that actually calls the main method present in a java code. JVM is a part of
JRE (Java Runtime Environment)
Java applications are called WORA (Write Once Run Anywhere). This means a
programmer can develop Java code on one system and can expect it to run on any
other Java-enabled system without any adjustment. This is all possible because of
JVM
Attention reader! Don't stop learning now. Get hold of all the important Java
Foundation and Collections concepts with the Fundamentals of Java and Java
Collections Course at a student-friendly price and become industry ready. To
complete your preparation from learning a language to DS Algo and many more,
please refer Complete Interview Preparation Course.
When we compile a java file, .class files(contains byte-code) with the same class
names present in ava file are generated by the Java compiler. This .class file goes into
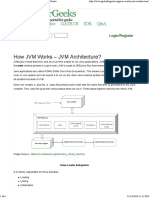
various steps when we run it. These steps together describe the whole JVM�JVM Language
Classes
Class Loader
JVM Memory
VM Language} JPC Native
Native Method Native Method
Class Loader Subsystem
Itis mainly responsible for three activities.
* Loading
* Linking
* Initialization
Loading: The Class loader reads the ".class” file, generate the corresponding binary
data and save it in the method area. For each “.class” file, JVM stores the following
information in the method area.
* The fully qualified name of the loaded class and its immediate parent class.
* Whether the ".class"file is related to Class or Interface or Enum�* Modifier, Variables and Method information etc.
After loading the “.class”file, JVM creates an object of type Class to represent this file
in the heap memory. Please note that this object is of type Class predefined in
java.lang package. These Class object can be used by the programmer for getting
class level information like the name of the class, parent name, methods and variable
information etc. To get this object reference we can use getClass() method of Object
class.
Java
71 A Java program to demonstrate working
// of a Class type object created by JVM
// to represent .class file in memory.
import java. lang.reflect. Field;
import java.lang.reflect Method;
// Java code to demonstrate use
// of Class object created by JVM
public class Test {
public static void main(String[] args)
{
Student s1 = new Student();
// Getting hold of Class
// object created by JVM.
Class cl = si.getClass();
// Printing type of object using cl.
System. out.println(c1.getName()) 5
// getting all methods in an array
Method m[] = c1.getDeclaredMethods();
for (Method method : m)
system. out. print1n(method.getName()) 5
// getting all fields in an array
Field f[] - cl.getDeclaredFields();
for (Field field : f)
system. out.print1n(field.getName());
+
71 A sample class whose information
1/ is fetched above using its Class object.
jass Student {
private String name;
private int roll_No;�public
public
public
public
t
String getName() { return name; }
void setName(String name) { this.name
int getRoll_no() { return roll_No; }
void setRoll_no(int roll_no)
‘this.roll_No = roll_no;
+
Output
student
getName
setName
getRoll_no
setRoll_no
name
roll_No
= name; )
Note: For every loaded “.classfile, only one object of the class is created
Student s2 = new Student();
// c2 will point to same object where
// cl is pointing
Class c2 = s2.getClass();
System. out.printIn(ci==c2); // true
Linking: Performs verification, preparation, and (optionally) resolution
Verification: It ensures the correctness of the .class file i.e. it checks whether this
file is properly formatted and generated by a valid compiler or not. If verification
fails, we get run-time exception java.lang. VerifyError. This activity is done by the
component ByteCodeVerifier. Once this activity is completed then the class file is
ready for compilation
Preparation: JVM allocates memory for class variables and initializing the memory
to default values.
Resolution: It is the process of replacing symbolic references from the type with
direct references.
referenced entity
It is done by searching into the method area to locate the�I
in the code and static block(if any). This is executed from top to bottom in a class and
jalization: |n this phase, all static variables are assigned with their values defined
from parent to child in the class hierarchy,
In general, there are three class loaders
* Bootstrap class loader. Every JVM implementation must have a bootstrap class
loader, capable of loading trusted classes. It loads core java API classes present in
the "JAVA_HOME/jre/lib" directory. This path is popularly known as the bootstrap
path, Itis implemented in native languages like C, C++.
* Extension class loader. Itis a child of the bootstrap class loader. It loads the classes
present in the extensions directories “JAVA_HOME/jre/lib/ext”(Extension path) or
any other directory specified by the java.ext.dirs system property. It is implemented
in java by the sun.misc. Launcher$ExtClassLoader class
* System/Application class loader. It is a child of the extension class loader. It is
responsible to load classes from the application classpath. It internally uses
Environment Variable which mapped to java.class.path. It is also implemented in
Java by the sun.misc.Launcher$AppClassloader class.
Java
// Java code to demonstrate Class Loader subsystem
public class Test {
public static void main(String[] args)
{
// String class is loaded by bootstrap loader, and
// bootstrap loader is not Java object, hence null
System. out.print1n(String. class.getClassLoader());�// Test class is loaded by Application loader
system. out.println(Test.class.getClassLoader());
Output
null
jdk. internal, loader. ClassLoaders$AppClassLoader@8bccS5f
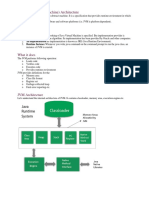
Note: JVM follows the Delegation-Hierarchy principle to load classes. System class
loader delegate load request to extension class loader and extension class loader
delegate request to the bootstrap class loader. If a class found in the boot-strap path,
the class is loaded otherwise request again transfers to the extension class loader and
then to the system class loader, At last, if the system class loader fails to load class,
then we get run-time exception java. lang. ClassNotFoundException
Classis loaded by
Go Class Loader
Class is loaded by
Goons Class Loader
BootStrap ClassLoader
Load Class}
[Extension ClassLoader
Load Class} Load Class
JVM Memory
1. Method area: In the method area, all class level information like class name,
immediate parent class name, methods and variables information etc. are stored,
including static variables. There is only one method area per JVM, and it is a shared
resource
2. Heap area: Information of all objects is stored in the heap area. There is also one
Heap Area per JVM. Itis also a shared resource.
Stack area: For every thread, JVM creates one run-time stack which is stored here
Every block of this stack is called activation record/stack frame which stores�methods calls. All local variables of that method are stored in their corresponding
frame. After a thread terminates, its run-time stack will be destroyed by JVM. Itis
not a shared resource
4. PC Registers: Store address of current execution instruction of a thread. Obviously,
each thread has separate PC Registers.
5. Native method stacks: For every thread, a separate native stack is created. It
stores native method information.
Execution Engine
Execution engine executes the “.class” (bytecode). It reads the bytecode line by line,
uses data and information present in various memory area and executes instructions
It can be classified into three parts:
* Interpreter. |t interprets the bytecode line by line and then executes, The
disadvantage here is that when one method is called multiple times, every time
interpretation is required
© Just-In-Time Compiler(JIT) : itis used to increase the efficiency of an interpreter. It
compiles the entire bytecode and changes it to native code so whenever the
interpreter sees repeated method calls, JIT provides direct native code for that part
so re-interpretation is not required, thus efficiency is improved.
* Garbage Collector. It destroys un-referenced objects. For more on Garbage
Collector, refer Garbage Collector.
“qa Native Interface (JNI) :
«(is an interface that interacts with the Native Method Libraries and provides the
native libraries(C, C++) required for the execution. It enables JVM to call C/C++�libraries and to be called by C/C++ libraries which may be specific to hardware
Native Method Libraries :
It is a collection of the Native Libraries(C, C++) which are required by the Execution
Engine
How Java Works? | GeeksforGeeks
This article is contributed by Gaurav Miglani. If you like GeeksforGeeks and would like
to contribute, you can also write an article using write.geeksforgeeks.org or mail your
article to contribute@geeksforgeeks.org. See your article appearing on the
GeeksforGeeks main page and help other Geeks.
Please write comments if you find anything incorrect, or you want to share more
information about the topic discussed above
Like 0�Previous
RECOMMENDED ARTICLES
0)1 Does JVM create object of Main
class (the class with main)?
06, Apr 16
0 2 Differences between JDK, JRE and 0 6
JVM
29, Jul?
013. Verification in Java vM)
06, Dec 17
04 Java Virtual Machine (JVM) Stack
Area
01, Feb 18
Article Contributed By :
© GeeksforGeeks
Vote for difficulty
Current difficulty : Medium
Fasy Normal = Medium = Hard
Next
Page: 1 2 3
How many types of memory areas
are allocated by JVM?
28, Jun 19
Types of JVM Garbage Collectors in
Java with implementation details
22, Jan 20
How to Generate JVM Heap
Memory Dump?
15, Jul21
Difference Between JVM and DVM.
27, Dec 20�Improved By: Akanksha_Rai, sambitdasi996, Lijulius, vikramboya
Article Tags: java-basics, java-JVM, Java, School Programming
Practice Tags: Java
Improve Article
Writing code in comment? Please use ide.geeksforgeeks.org, generate link and share the link here,
Load Comments
oS GeeksforGeeks
Sth Floor, A-118,
Sector-136, Noida, Uttar Pradesh - 201305
feedback@geeksforgeeks.org
Company Learn
‘About Us Algorithms
Careers Data Structures
Privacy Policy Languages
Contact Us CS Subjects
Copyright Policy Video Tutorials
Web Development Contribute
Web Tutorials Write an Article
HTML Write Interview Experience
css Internships
Javascript Videos
Bootstrap�@geeksforgeeks , Some rights reserved