0% found this document useful (0 votes)
351 views42 pagesCCNA Lab: Cisco Router Basics
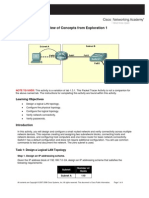
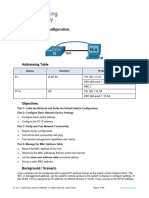
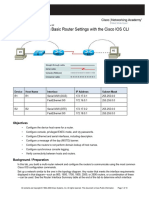
This document provides instructions for a CCNA lab exercise on configuring IPv4 addressing on a Cisco router. The lab scenario has the student configure IP addresses on serial and fast ethernet interfaces to connect the router to other devices and subnets. Specifically, the student must set IP addresses on serial interfaces to connect to routers at specific IP addresses, assign IP addresses to fast ethernet interfaces for subnets with specified numbers of hosts, and configure host and gateway IPs. The goal is to test connectivity by having hosts ping a server IP address.
Uploaded by
MitraCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd
0% found this document useful (0 votes)
351 views42 pagesCCNA Lab: Cisco Router Basics
This document provides instructions for a CCNA lab exercise on configuring IPv4 addressing on a Cisco router. The lab scenario has the student configure IP addresses on serial and fast ethernet interfaces to connect the router to other devices and subnets. Specifically, the student must set IP addresses on serial interfaces to connect to routers at specific IP addresses, assign IP addresses to fast ethernet interfaces for subnets with specified numbers of hosts, and configure host and gateway IPs. The goal is to test connectivity by having hosts ping a server IP address.
Uploaded by
MitraCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd
/ 42