0% found this document useful (0 votes)
109 views19 pagesChapter 3-2 Io Address Decoding and Design
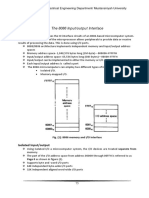
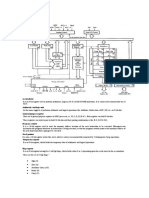
This document discusses I/O address decoding and design. It begins by introducing the use of the 74LS373 and 74LS244 chips for building output and input ports. It then covers absolute versus linear address decoding and peripheral I/O versus memory-mapped I/O. Examples are provided to illustrate designing output and input ports for memory-mapped I/O systems using the 74LS373 and 74LS244 chips.
Uploaded by
Sama A ShurrabCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd
0% found this document useful (0 votes)
109 views19 pagesChapter 3-2 Io Address Decoding and Design
This document discusses I/O address decoding and design. It begins by introducing the use of the 74LS373 and 74LS244 chips for building output and input ports. It then covers absolute versus linear address decoding and peripheral I/O versus memory-mapped I/O. Examples are provided to illustrate designing output and input ports for memory-mapped I/O systems using the 74LS373 and 74LS244 chips.
Uploaded by
Sama A ShurrabCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd
/ 19