0% found this document useful (0 votes)
362 views50 pagesLecture 1 - Fundamentals of Engineering Drawing
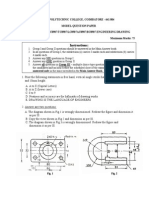
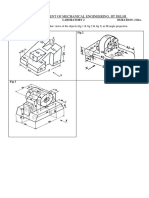
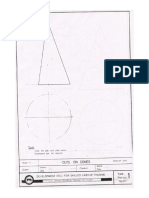
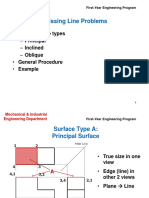
The document discusses a lecture on engineering drawing and graphics fundamentals. It covers topics like the course outline, introduction to graphics language, traditional drawing tools, drawing standards, and scales. Engineering drawing is presented as a universal language for engineers to visualize designs, communicate solutions, and document designs.
Uploaded by
Zeeshan AhmedCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd
0% found this document useful (0 votes)
362 views50 pagesLecture 1 - Fundamentals of Engineering Drawing
The document discusses a lecture on engineering drawing and graphics fundamentals. It covers topics like the course outline, introduction to graphics language, traditional drawing tools, drawing standards, and scales. Engineering drawing is presented as a universal language for engineers to visualize designs, communicate solutions, and document designs.
Uploaded by
Zeeshan AhmedCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd
/ 50