0% found this document useful (0 votes)
1K views6 pages03 Task Performance 1
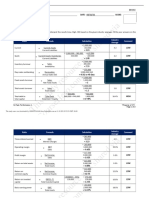
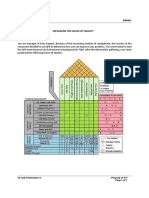
This document provides guidelines and requirements for developing a business plan as part of an entrepreneurial management course. It outlines the key sections that must be included in the business plan such as the executive summary, organizational background with vision, mission and values statements, and description of proposed products/services. The document also lists some business categories and tips for generating business ideas such as leveraging personal skills, current market trends, fulfilling unmet needs, and improving existing products. Students are asked to craft the initial sections of a business plan for a new venture within one of the categories presented.
Uploaded by
Princess ParasCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd
0% found this document useful (0 votes)
1K views6 pages03 Task Performance 1
This document provides guidelines and requirements for developing a business plan as part of an entrepreneurial management course. It outlines the key sections that must be included in the business plan such as the executive summary, organizational background with vision, mission and values statements, and description of proposed products/services. The document also lists some business categories and tips for generating business ideas such as leveraging personal skills, current market trends, fulfilling unmet needs, and improving existing products. Students are asked to craft the initial sections of a business plan for a new venture within one of the categories presented.
Uploaded by
Princess ParasCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd
/ 6