0% found this document useful (0 votes)
61 views2 pagesWhat Is Charging by Induction and How Does It Occur? How Can The Results of Charging by Induction Be Predicted and Explained?
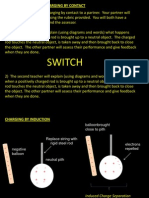
The document discusses charging by induction, where bringing a charged object near a neutral object causes the opposite charge to be induced. It provides examples using balloons and metal objects to demonstrate how the process works in two steps - first inducing opposite charges, then allowing a ground to remove excess charge and leave the object charged.
Uploaded by
Mico James TrillesCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd
0% found this document useful (0 votes)
61 views2 pagesWhat Is Charging by Induction and How Does It Occur? How Can The Results of Charging by Induction Be Predicted and Explained?
The document discusses charging by induction, where bringing a charged object near a neutral object causes the opposite charge to be induced. It provides examples using balloons and metal objects to demonstrate how the process works in two steps - first inducing opposite charges, then allowing a ground to remove excess charge and leave the object charged.
Uploaded by
Mico James TrillesCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd
/ 2