0% found this document useful (0 votes)
108 views6 pagesExperiment 5 - Functions in DBMS
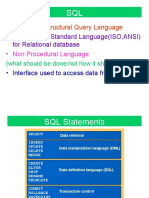
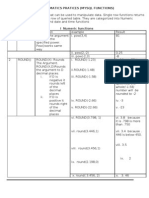
1) The document provides instructions for an experiment on studying and implementing numeric, character, aggregate, and group by functions in a database system.
2) It describes various date, numeric, and character functions including sysdate, add_months, last_day, months_between, next_day, abs, sqrt, greatest, least, ceil, floor, power, round, trunc, lower, upper, to_char, and to_date.
3) It also explains aggregate/group functions like avg, min, max, sum, and using the group by clause to divide rows into groups and calculate statistics for each group. Problems involving retrieving data based on these functions are provided.
Uploaded by
Ajay ZagadeCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd
0% found this document useful (0 votes)
108 views6 pagesExperiment 5 - Functions in DBMS
1) The document provides instructions for an experiment on studying and implementing numeric, character, aggregate, and group by functions in a database system.
2) It describes various date, numeric, and character functions including sysdate, add_months, last_day, months_between, next_day, abs, sqrt, greatest, least, ceil, floor, power, round, trunc, lower, upper, to_char, and to_date.
3) It also explains aggregate/group functions like avg, min, max, sum, and using the group by clause to divide rows into groups and calculate statistics for each group. Problems involving retrieving data based on these functions are provided.
Uploaded by
Ajay ZagadeCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd
/ 6