0% found this document useful (0 votes)
169 views12 pagesCar Evaluation Data Analysis & Random Forest Model
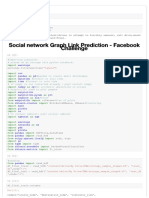
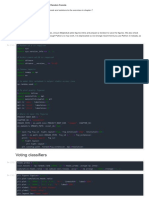
This document summarizes the preprocessing steps for a machine learning model to classify car evaluations:
1) The data is read from a CSV file and split into feature (X) and target (y) variables.
2) The data is split into training and test sets.
3) Categorical variables are encoded using ordinal encoding to prepare for modeling.
Uploaded by
Prajith SprinťèřCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd
0% found this document useful (0 votes)
169 views12 pagesCar Evaluation Data Analysis & Random Forest Model
This document summarizes the preprocessing steps for a machine learning model to classify car evaluations:
1) The data is read from a CSV file and split into feature (X) and target (y) variables.
2) The data is split into training and test sets.
3) Categorical variables are encoded using ordinal encoding to prepare for modeling.
Uploaded by
Prajith SprinťèřCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd
/ 12