MODULE IN ABM 12
ENTREPRENEURSP
Second Quarter
Week 5
MOST ESSENTIAL LEARNING COMPETENCY
The learner demonstrates understanding of concepts, underlying principles, and processes of starting and
operating a simple business. - CS_EP11/12BENTREP-IVa-i-1
OBJECTIVES
manifest understanding of starting and operating a simple business;
implement the marketing plan and strategies.
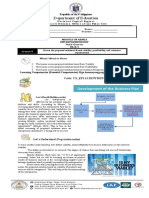
IMPLEMENTATION OF BUSINESS PLAN
What’s In
Even the most well-thought-out business plan is just a piece of paper if it doesn’t have a plan for
implementation. This is the portion of the business plan where objectives are clarified, tasks are assigned with
deadlines, and program is charted to reach goals and milestones.
A. Guidelines for successful business plan implementation
1. Objectives
⮚ The objectives should be crystal clear and specifically spelled out,
since it will be used as a building block for the rest of the
implementation plan.
⮚ The objective should be tough but reachable and could read.
something like this:
❖ Secure office space and be open for business in three months.
❖ Sign three clients within the first three months of operations.
❖ Sign 10 clients within the first year.
2. Tasks
⮚ This part details what must be accomplished to achieve the objectives.
⮚ Include a task manager for each step, so that roles are clearly defined and there is accountability.
⮚ Enumerate tasks and assignments, with descriptions specifically plainly and generally stated; without
getting into a step-by-step, micromanaged explanation of how the tasks will be carried out.
⮚ Emphasize the expected results associated with these tasks.
⮚ The tasks section might read like this:
❖ Secure office space – real estate agent
❖ Obtain licenses and permits – you.
❖ Set up office phones and computers – office manager.
❖ Begin recruiting clients – sales manager.
❖ Create marketing collateral – marketing manager.
❖ Solicit referrals from clients – relationship manager.
3. Time Allocation
⮚ Each task should be paired with an appropriate time frame for completion.
⮚ The time allocation should be aggressive but reasonable in order to ensure not just completion but
competent work. For assistance in framing this timescale, use a program such as Microsoft Project,
or just create your own Gantt chart – a helpful tool that shows how long it will take to complete
different tasks and in what order the tasks should be finished.
4. Progress
⮚ The overall management team leader needs to be in charge of monitoring each task’s progress and
the completion percentage of each objective.
⮚ When delays occur, try to get to the root of the problem.
� ❖ Did the person responsible drop the ball?
❖ Did he or she have too many responsibilities to handle?
❖ Did a third party, such as a supplier or the bank fail to hold up its end of the deal?
⮚ Adjust the Gantt chart appropriately to account for the delay, a make note of the previous deadline
and the reason it was missed.
⮚ The more efficient the start of the implementation of the business plan is, the more likely it will
survive in the early period.
B. Operating the Business
● Before starting a business, aspiring entrepreneurs should seek professional advice from small
enterprise advisors, accountants or consultants on what is the best type of enterprise to establish,
as this varies according to the legal framework and economic structures prevailing at a given time.
● The form that a business takes is influenced by both the wishes or needs of the owner and also by
the types of products that are to be made. It is usually simpler and cheaper to register either as a
personal business with single owner/director. However, this may not be appropriate if additional
partners are required to contribute capital specific skills.
● Other type of business that can therefore be considered include a partnership or if the proposed
enterprise has a larger number of interested investors, the form of the business could be cooperative
association, a not-for-profit organization or a corporation.
C. Business Registration Requirements
The following are the basic requirements to start commencing a business.
in the Philippines:
❖ SEC registration – for partnership or corporation
❖ DTI registration – for registering your business trade name.
❖ Mayor’s business permit – for getting the license to operate in the city or municipality and payment
of your local business taxes.
❖ BIR registration – for getting TIN, official receipts and invoices, registering your book of accounts,
and paying your national internal revenue taxes (Income tax, VAT or Percentage Tax, Withholding
taxes, etc.)
❖ SSS, Philhealth, and Pag-Ibig Fund registration – for registering yourself or company as an employer
and for remitting your employees’ contribution together with your employer’s share.
Usually, the BIR and the City/Municipality Office require the certificates of registration with the SEC or
DTI before a business can be registered to these agencies. Thus, there is a need to register through these
offices to start the business.
D. Special Requirements
Aside from the basic requirements, there are also special licenses or
registrations that must be obtained by a business to start its operation.
For example:
1. Banks, financing company, lending company, pawnshops, money changers, money remittance
business, and other financing institutions are required to be registered with the Bangko Sentral ng
Pilipinas (BSP).
2. If you are manufacturing and selling products related to food and drugs, you also have to register with
Bureau of Food and Drugs (BFAD).
3. For schools and entities involved in providing education, they should register with the Commission on
Higher Education (CHED) and Department of Education (Deped).
E. Other Steps to Follow Before Operating a Business
1. Set up an accounting system or hire an accountant. Knowing how the business is doing financially is
important for planning and survival. Using an accounting software will make tracking business
transactions easier.
2. Advertise the business. No one will buy the products or services if the customers don’t know that the
company exists. Create a website and advertise in different media, such as newspapers and radio. Ask
customers for referrals. Network with other business owners which will help in the recognition and
gain referrals for the new business.
3. Secure insurance for the business. Liability insurance protects the business in the event of litigation.
Consider life and disability insurance, health insurance, insurance, if you are leasing an office or
storefront.