0% found this document useful (0 votes)
86 views20 pagesSocialization: Context and Impact
This document discusses socialization and its key elements. It begins by having the reader look back on their childhood interactions with family, relatives, neighbors, and godparents. It then outlines the objectives of identifying the context, content, processes, and consequences of socialization.
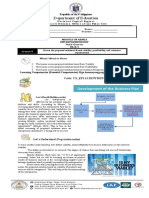
The document defines socialization as how people acquire personality and learn the way of life of their society. It discusses the biological and psychological contexts of socialization. The content of socialization includes ideas, beliefs, behaviors, and other information passed between members. The processes include primary, secondary, resocialization, and reverse socialization. Key consequences are establishing a self-concept, developing the capacity for role-taking, and acting in socially acceptable ways.
Uploaded by
Cathleenbeth MorialCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd
0% found this document useful (0 votes)
86 views20 pagesSocialization: Context and Impact
This document discusses socialization and its key elements. It begins by having the reader look back on their childhood interactions with family, relatives, neighbors, and godparents. It then outlines the objectives of identifying the context, content, processes, and consequences of socialization.
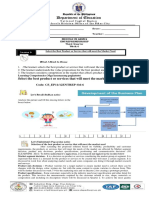
The document defines socialization as how people acquire personality and learn the way of life of their society. It discusses the biological and psychological contexts of socialization. The content of socialization includes ideas, beliefs, behaviors, and other information passed between members. The processes include primary, secondary, resocialization, and reverse socialization. Key consequences are establishing a self-concept, developing the capacity for role-taking, and acting in socially acceptable ways.
Uploaded by
Cathleenbeth MorialCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd
/ 20