0% found this document useful (0 votes)
3K views10 pagesDSP Syllabus
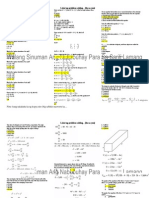
This document outlines a course on digital signal processing (DSP) systems. The course objectives are to make students aware of signal and system properties and their real-world applications, and familiarize students with important DSP methods like digital filter design and transform-domain processing. The course outcomes are for students to analyze signals and systems using concepts like the Fourier transform, design and implement digital filters, integrate DSP tools, and apply signal processing strategies to multi-disciplinary problems. The syllabus covers topics like discrete-time signals and systems, the Fourier and z-transforms, fast Fourier transforms, and filter design. Student performance is evaluated based on assignments, exams, lab work, and a project.
Uploaded by
Prathamesh MoreCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd
0% found this document useful (0 votes)
3K views10 pagesDSP Syllabus
This document outlines a course on digital signal processing (DSP) systems. The course objectives are to make students aware of signal and system properties and their real-world applications, and familiarize students with important DSP methods like digital filter design and transform-domain processing. The course outcomes are for students to analyze signals and systems using concepts like the Fourier transform, design and implement digital filters, integrate DSP tools, and apply signal processing strategies to multi-disciplinary problems. The syllabus covers topics like discrete-time signals and systems, the Fourier and z-transforms, fast Fourier transforms, and filter design. Student performance is evaluated based on assignments, exams, lab work, and a project.
Uploaded by
Prathamesh MoreCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd
/ 10