0% found this document useful (0 votes)
345 views28 pagesComputer Graphics Practical Guide
The document contains 10 programming assignments related to computer graphics concepts like drawing lines, circles, ellipses and rotating/translating triangles using various algorithms. The assignments include writing programs to:
1) Draw a line using DDA and Bresenham's line drawing algorithms.
2) Draw a circle using Bresenham's circle drawing algorithm.
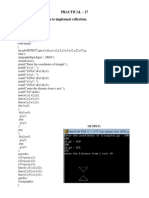
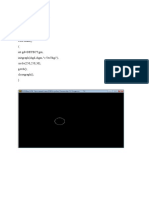
3) Draw an ellipse using the midpoint ellipse drawing algorithm.
4) Rotate, scale and translate triangles.
5) Rotate a point about the origin and about another point.
6) Show line clipping.
The document provides sample code for some of the assignments.
Uploaded by
Saif AliCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd
0% found this document useful (0 votes)
345 views28 pagesComputer Graphics Practical Guide
The document contains 10 programming assignments related to computer graphics concepts like drawing lines, circles, ellipses and rotating/translating triangles using various algorithms. The assignments include writing programs to:
1) Draw a line using DDA and Bresenham's line drawing algorithms.
2) Draw a circle using Bresenham's circle drawing algorithm.
3) Draw an ellipse using the midpoint ellipse drawing algorithm.
4) Rotate, scale and translate triangles.
5) Rotate a point about the origin and about another point.
6) Show line clipping.
The document provides sample code for some of the assignments.
Uploaded by
Saif AliCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd
/ 28