Unit 1 (Lesson 1): SUMMARIZING THE FUNCTIONALITY OF EMPLOYEE CENTRAL
- Employee Central basics:
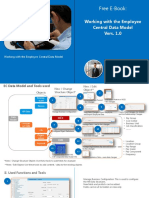
SAP SuccessFactors Employee Central provides a reliable, consistent system of record
for global companies and helps enhance the overall experience for highly diverse mobile
employees. It makes tasks less manual for employees, managers, and HR, giving them the tools
to automate time-consuming tasks.
SAP SuccessFactors Employee Central Core features allow for an easy-to-configure
Organization, Job, and Pay structure, customize Employee Data elements, and provide for Event
and Event Reasons to track what is happening throughout the employee lifecycle. You can
automate a workflow for each event reason to standardize the approval process. The system
includes robust tools for data import, mass changes, and rule management.
Unit 2: CONFIGURING INITIAL ELEMENTS
Lesson 1: Using XML during data model configuration
SAP SuccessFactors Employee Central Core structure:
+ Foundation Objects is a fundamental aspect of Employee Central. Foundation Objects
allow the company to define and store its organization, pay, and job structures, which helps
organize employee information. Some of these objects are managed through the Metadata
Framework as MetaData Framework (MDF) Objects, while XML-based objects are managed
through Corporate Data Model.
+ Another important component of Employee Central is the HR data structure.
Employee Central stores personal employee information, such as date of birth and national ID,
and employment information, such as job title and salary.
+ One of the key features of SAP SuccessFactors is the ease with which you can maintain
data. The solution offers both employee and manager self-service. This feature is controlled
through role-based permissions (RBP) that allow you to decide who can view and edit data in
the system. Managers and employees can initiate changes to their data or their subordinate’s
data.
C1 - INTERNAL
� Data models in SAP SuccessFactors Employee Central:
Data Models describe how data elements are structured in a database. They also define
the properties these elements possess and their relationships to each other.
Example:
Data Model Configuration:
The data models in SAP SuccessFactors Employee Central play a critical role in
configuring customer requirements. You have already seen an example of visibility and custom
labels in the interaction, Person Info Element. Remember that you could not see the Date of
Death field and that the Place of Birth field was relabeled to the City of Birth. When configuring
the data models, you can:
C1 - INTERNAL
� ● Set the visibility of a field in the instance.
● Define custom labels and fields.
● Define the relationship among Foundation Objects.
● Set the order of fields that appear in the instance.
● Set a picklist for a field
Any changes made in the data model must comply with the Data Type Definition (DTD).
That means you cannot add a new element, field, or attribute unless it is defined in the DTD.
When a particular field is not needed in the configuration, we recommend you hide the field
rather than delete it from the data model. If it must be deleted, for whatever reason, we
recommend you set the visibility to "none" before deleting the field.
The Four Data Models:
The Succession Data Model (SDM) controls the underlying information structure you see
on the People Profile. The different elements defined in SDM are used across different SAP
SuccessFactors solutions. The relevant element for Employee Central is the HRIS element. An
employee record is divided into two main areas, Employment, and Personal Information:
+ Employment Information houses a record of the employee at work, including job
information, compensation information, etc.
+ Personal Information contains a record of the employee outside of work, including the
home address, national ID, and contact information.
Additionally, the Employment and Personal Information records can store country-
specific information. For example, a company might record Equal Employment Opportunity
(EEO) or Fair Labor Standards Act (FLSA) information in the USA or different kinds of national
IDs.
C1 - INTERNAL
�C1 - INTERNAL