Unit 2 (Cloud Computing Architecture)
Uploaded by
Binay YadavUnit 2 (Cloud Computing Architecture)
Uploaded by
Binay YadavCloud Computing -RJU
Unit 2
Cloud Computing Architecture
Cloud computing architecture is simple; it clearly states the components and subcomponents embedded in
it There’s no question that cloud computing is here to stay. It touches every part of our lives today,
offering many advantages in terms of flexibility, storage, sharing, maintenance, and much more.
A standard internet connection or a virtual network provides us access to cloud-based applications and
services like Google Docs, Skype, and Netflix. Most companies are shifting their businesses into the
cloud as they require significant storage, which cloud platforms provide. A cloud computing architecture
provides higher bandwidth to its users due to which data over the cloud can be used from anywhere across
the world at any time. Due to its architecture, it not only shares resources among client source consumers
but also with open-source communities like Microsoft and Red hat.
Cloud Computing Architecture is divided into two parts, i.e., front-end and back-end. Front-end and
back-end communicate via a network or internet. A diagrammatic representation of cloud computing
architecture is shown below:
Cloud Computing Architecture
Front-End
It provides applications and the interfaces that are required for the cloud-based service.
It consists of client’s side applications, which are web browsers such as Google Chrome and Internet
Explorer.
Cloud infrastructure is the only component of the front-end.
Cloud infrastructure consists of hardware and software components such as data storage, server,
virtualization software, etc.
It also provides a Graphical User Interface to the end-users to perform respective tasks.
Back-End
It is responsible for monitoring all the programs that run the application on the front-end
It has a large number of data storage systems and servers. The back-end is an important and huge part of
the whole cloud computing architecture, as shown below:
The components of the back-end cloud architecture are mentioned below. Let's understand them in detail
one by one.
Er.Binay Yadav Page 1
Cloud Computing -RJU
Application
It can either be a software or a platform
Depending upon the client requirement, the application provides the result to the end- user (with
resources) in the back end.
Service
Service is an essential component in cloud architecture
Its responsibility is to provide utility in the architecture
In a Cloud, few widely used services among the end-users are storage application
development environments and web services
Storage
It stores and maintains data like files, videos, documents, etc. over the internet
Some of the popular examples of storage services are below:
Amazon S3
Oracle Cloud-Storage
Microsoft Azure Storage
Its capacity varies depending upon the service providers available in the market
Management
Its task is to allot specific resources to a specific task, it simultaneously performs various
functions of the cloud environment.
It helps in the management of components like application, task, service, security, data storage,
and cloud infrastructure
In simple terms, it establishes coordination among the cloud resources
Security
Security is an integral part of back-end cloud infrastructure
It provides secure cloud resources, systems, files, and infrastructure to end-users
Also, it implements security management to the cloud server with virtual firewalls which
results in preventing data loss
Benefits of Cloud Computing Architecture
The cloud computing architecture is designed in such a way that:
It solves latency issues and improves data processing requirements
It reduces IT operating costs and gives good accessibility to access data and digital tools
It helps businesses to easily scale up and scale down their cloud resources
It has a flexibility feature which gives businesses a competitive advantage
It results in better disaster recovery and provides high security
It automatically updates its services
It encourages remote working and promotes team collaboration
Cloud Computing Architecture Components
Some of the important components of Cloud Computing architecture that we will be looking into are as
follows:
Hypervisor
Management Software
Deployment Software
Network
Cloud Server
Cloud Storage
Er.Binay Yadav Page 2
Cloud Computing -RJU
Components of Cloud architecture
Hypervisor
It is a virtual machine monitor which provides Virtual Operating Platforms to every user
It also manages guest operating systems in the cloud
It runs a separate virtual machine on the back end which consists of software and hardware
Its main objective is to divide and allocate resources
Management Software
Its responsibility is to manage and monitor cloud operations with various strategies to increase the
performance of the cloud
Some of the operations performed by the management software are:
compliance auditing
management of overseeing disaster
contingency plans
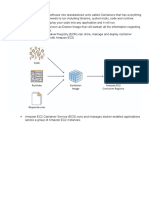
Deployment Software
It consists of all the mandatory installations and configurations required to run a cloud service
All deployment of cloud services is performed using a deployment software
The three different models which can be deployed are the following:
Er.Binay Yadav Page 3
Cloud Computing -RJU
SaaS - Software as a service hosts and manages applications of the end-user. Example: Gmail
PaaS - Platform as a service helps developers to build, create, and manage
applications.
Example: Microsoft Azure
IaaS - Infrastructure as a service provides services on a pay-as-you-go pricing model.
NETWORK
It connects the front-end and back-end. Also, allows every user to access cloud resources
It helps users to connect and customize the route and protocol
It is a virtual server which is hosted on the cloud computing platform
It is highly flexible, secure, and cost-effective
Cloud Storage
Here, every bit of data is stored and accessed by a user from anywhere over the internet
It is scalable at run-time and is automatically accessed
Data can be modified and retrieved from cloud storage over the web
Cloud Reference Model
The reference model for cloud computing is an abstract model that characterizes and standardizes a cloud
computing environment by partitioning it into abstraction layers and cross- layer functions.
Er.Binay Yadav Page 4
Cloud Computing -RJU
IaaS | Infrastructure as a Service
1. IaaS stands for infrastructure as a service.
2. Infrastructure as service or IaaS is the basic layer in cloud computing model.
3. IaaS offers servers, network devices, load balancers, database, Web servers etc.
4. IaaS delivers customizable infrastructure on demand.
5. IaaS examples can be categorized in two categories
6. IaaS Management layer
7. IaaS Physical infrastructure
8. Some service providers provide both above categories and some provides only management layer.
9. IaaS management layer also required integration with other IaaS solutions that provide physical
infrastructure.
10. On virtual machines applications are installed and deployed.
11. One of the examples of virtual machine is Oracle VM.
12. Hardware virtualization includes workload partitioning, application isolation,
sandboxing, and hardware tuning.
13. Instead of purchasing user can access these virtual hardware’s on pay per use basis.
14. users can take advantage of the full customization offered by virtualization to deploy their
infrastructure in the cloud.
15. Some virtual machines can be with pre-installed operating systems and other software’s.
16. On some virtual machines operating systems and others software’s can be installed as per use.
Some examples:
1. Amazon Web Services (AWS),
2. Microsoft Azure,
3. Google Compute Engine (GCE)
Er.Binay Yadav Page 5
Cloud Computing -RJU
Characteristics of IaaS
There are the following characteristics of IaaS -
Resources are available as a service
Services are highly scalable
Dynamic and flexible
GUI and API-based access
Automated administrative tasks
IaaS provider provides the following services -
1. Compute: Computing as a Service includes virtual central processing units and virtual main
memory for the Vms that is provisioned to the end- users.
2. Storage: IaaS provider provides back-end storage for storing files.
3. Network: Network as a Service (NaaS) provides networking components such as routers,
switches, and bridges for the Vms.
4. Load balancers: It provides load balancing capability at the infrastructure layer.
Er.Binay Yadav Page 6
Cloud Computing -RJU
Advantages of IaaS cloud computing layer
There are the following advantages of IaaS computing layer -
1. Shared infrastructure
IaaS allows multiple users to share the same physical infrastructure.
2. Web access to the resources
Iaas allows IT users to access resources over the internet.
3. Pay-as-per-use model
IaaS providers provide services based on the pay-as-per-use basis. The users are required to pay
for what they have used.
4. Focus on the core business
IaaS providers focus on the organization's core business rather than on IT infrastructure.
5. On-demand scalability
On-demand scalability is one of the biggest advantages of IaaS. Using IaaS, users do not worry
about to upgrade software and troubleshoot the issues related to hardware components.
Disadvantages of IaaS cloud computing layer
1. Security
Security is one of the biggest issues in IaaS. Most of the IaaS providers are not able to provide
100% security.
2. Maintenance & Upgrade
Although IaaS service providers maintain the software, but they do not upgrade the software for
some organizations.
3. Interoperability issues
It is difficult to migrate VM from one IaaS provider to the other, so the customers might face
problem related to vendor lock-in.
Top Iaas Providers who are providing IaaS cloud computing platform
Er.Binay Yadav Page 7
Cloud Computing -RJU
IaaS Vendor Iaas Solution Details
Amazon Web Elastic, Elastic Compute The cloud computing platform pioneer,
Services Cloud (EC2) MapReduce, Amazon offers auto scaling, cloud
Route 53, Virtual Private monitoring, and load balancing features as
Cloud, etc. part of its portfolio.
Netmagic Netmagic IaaS Cloud Netmagic runs from data centers in Mumbai,
Solutions Chennai, and Bangalore, and a virtual data
center in the United States. Plans are
underway to extend services to West Asia.
Rackspace Cloud servers, cloud files, The cloud computing platform vendor
cloud sites, etc. focuses primarily on enterprise-level hosting
services.
Reliance Reliance Internet Data RIDC supports both traditional hosting and
Communications Center cloud services, with data centers in Mumbai,
Bangalore, Hyderabad, and Chennai. The
cloud services offered by RIDC include IaaS
and SaaS.
Sify Technologies Sify IaaS Sify's cloud computing platform is powered
by HP's converged infrastructure. The
vendor offers all three types of cloud
services: IaaS, PaaS, and SaaS.
Tata InstaCompute InstaCompute is Tata Communications' IaaS
Communications offering. InstaCompute data centers are
located in Hyderabad and Singapore, with
operations in both countries.
PaaS | Platform as a service
1. PaaS stands for platform as a service.
2. PaaS provides a computing platform with a programming language execution environment.
3. PaaS provide a development and deployment platform for running applications in the cloud.
4. PaaS constitute the middleware on top of which applications are built.
5. Application management is the core functionality of the middleware.
6. PaaS provides run time environments for the applications.
7. PaaS provides
a. Applications deployment
b. Configuring application components
c. Provisioning and configuring supporting technologies
Er.Binay Yadav Page 8
Cloud Computing -RJU
8. For users PaaS interfaces can be in the form of a Web-based interface or in the form of programming
APIs and libraries.
9. PaaS solutions generally include the infrastructure as well.
10. Pure PaaS offered only the user-level middleware.
11. PaasS classification:
a. PaaS-I: Runtime environment with Web-hosted application development platform.
Rapid application prototyping. For example Force.com which is a combination of
middleware and infrastructure product type.
b. PaaS-II: Runtime environment for scaling Web applications. The runtime could be enhanced
by additional components that provide scaling capabilities. For example Google AppEngine
which is a combination of middleware and infrastructure product type. Appscale is
middlware product type.
c. PaaS-III: Middleware and programming model for developing distributed applications in the
cloud. For example Microsoft Azure which is a combination of middleware and infrastructure
product type. Manjrasoft Aneka is a middleware product type.
12. Some examples:
a. Google App Engine
b. Force.com
PaaS providers provide the Programming languages, Application frameworks, Databases, and Other tools:
Er.Binay Yadav Page 9
Cloud Computing -RJU
1. Programming languages
PaaS providers provide various programming languages for the developers to develop the
applications. Some popular programming languages provided by PaaS providers are Java,
PHP, Ruby, Perl, and Go.
2. Application frameworks
PaaS providers provide application frameworks to easily understand the application
development. Some popular application frameworks provided by PaaS providers are
Node.js, Drupal, Joomla, WordPress, Spring, Play, Rack, and Zend.
3. Databases
PaaS providers provide various databases such as ClearDB, PostgreSQL, MongoDB, and
Redis to communicate with the applications.
4. Other tools
PaaS providers provide various other tools that are required to develop, test, and deploy the
applications.
Characteristics of PaaS:
1. Runtime framework: The runtime framework executes end-user code according
to the policies set by the user and the provider.
2. Abstraction: PaaS offer a way to deploy and manage applications on the cloud rather
than a virtual machine on top of which the IT infrastructure is built and configured.
3. Automation: PaaS deploy the applications automatically.
4. Cloud services: Provide services for creation, delivery, monitoring
management, reporting of applications.
Advantages of PaaS
There are the following advantages of PaaS -
1) Simplified Development
PaaS allows developers to focus on development and innovation without worrying
about infrastructure management.
2) Lower risk
No need for up-front investment in hardware and software. Developers only need
a PC and an internet connection to start building applications.
3) Prebuilt business functionality
Some PaaS vendors also provide already defined business functionality so that users
can avoid building everything from very scratch and hence can directly start the
projects only.
4) Instant community
PaaS vendors frequently provide online communities where the developer can
Er.Binay Yadav Page 10
Cloud Computing -RJU
get the ideas to share experiences and seek advice from others.
5) Scalability
Applications deployed can scale from one to thousands of users without any changes
to the applications.
Disadvantages of PaaS cloud computing layer
1) Vendor lock-in
One has to write the applications according to the platform provided by the PaaS
vendor, so the migration of an application to another PaaS vendor would be a
problem.
2) Data Privacy
Corporate data, whether it can be critical or not, will be private, so if it is not
located within the walls of the company, there can be a risk in terms of privacy
of data.
3) Integration with the rest of the systems applications
It may happen that some applications are local, and some are in the cloud. So there
will be chances of increased complexity when we want to use data which in the
cloud with the local data.
Popular PaaS Providers
The below table shows some popular PaaS providers and services that are provided by them -
Er.Binay Yadav Page 11
Cloud Computing -RJU
Providers Services
Google App Engine App Identity, URL Fetch, Cloud storage client library, Logservice
(GAE)
Salesforce.com Faster implementation, Rapid scalability, CRM Services, Sales cloud,
Mobile connectivity, Chatter.
Windows Azure Compute, security, IoT, Data Storage.
AppFog Justcloud.com, SkyDrive, GoogleDocs
Openshift RedHat, Microsoft Azure.
Cloud Foundry from Data, Messaging, and other services.
VMware
SaaS | Software as a service
1. SaaS stands for software as a service.
2. Software as a service (SaaS) allows users to connect to and use cloud-based apps
over the Internet.
3. SaaS is the service with which end users interact directly.
4. It provides a means to free users from complex hardware and software management.
5. In SaaS customer do not new to purchase the software and required the license.
6. They simply access the application website, enter their credentials and billing
details, and can instantly use the application.
7. Customer can customize their software.
8. Application is available to the customer on demand.
9. SaaS can be considered as a “one-to-many” software delivery model.
10. In SaaS applications are built as per the user needs.
11. From the examples mentioned below we can find why SaaS is considered as one to
many models.
12. Some examples:
a. Gmail
b. Google drive
c. Dropbox
d. WhatsApp
Characteristics of SaaS:
1. The product sold to customer is application access.
2. The application is centrally managed.
3. The service delivered is one-to-many.
4. The service delivered is an integrated solution delivered on the contract, which
means provided as promised.
There are the following services provided by SaaS providers -
Business Services - SaaS Provider provides various business services to start-
up the business. The SaaS business services include ERP (Enterprise Resource
Planning), CRM (Customer Relationship Management), billing, and sales.
Er.Binay Yadav Page 12
Cloud Computing -RJU
Document Management - SaaS document management is a software application
offered by a third party (SaaS providers) to create, manage, and track electronic
documents.
Example: Slack, Samepage, Box, and Zoho Forms.
Social Networks - As we all know, social networking sites are used by the general
public, so social networking service providers use SaaS for their convenience and
handle the general public's information.
Mail Services - To handle the unpredictable number of users and load on e-mail
services, many e-mail providers offering their services using SaaS.
Advantages of SaaS cloud computing layer
1) SaaS is easy to buy
SaaS pricing is based on a monthly fee or annual fee subscription, so it allows
organizations to access business functionality at a low cost, which is less than licensed
applications.
Unlike traditional software, which is sold as a licensed based with an up-front cost (and
often an optional ongoing support fee), SaaS providers are generally pricing the
applications using a subscription fee, most commonly a monthly or annually fee.
2. One to Many
SaaS services are offered as a one-to-many model means a single instance of the application is
shared by multiple users.
3. Less hardware required for SaaS
The software is hosted remotely, so organizations do not need to invest in additional hardware.
4. Low maintenance required for SaaS
Software as a service removes the need for installation, set-up, and daily maintenance for the
organizations. The initial set-up cost for SaaS is typically less than the enterprise software.
SaaS vendors are pricing their applications based on some usage parameters, such as a
number of users using the application. So SaaS does easy to monitor and automatic updates.
Er.Binay Yadav Page 13
Cloud Computing -RJU
5. No special software or hardware versions required
All users will have the same version of the software and typically access it through the web
browser. SaaS reduces IT support costs by outsourcing hardware and software maintenance
and support to the IaaS provider.
6. Multidevice support
SaaS services can be accessed from any device such as desktops, laptops, tablets, phones,
and thin clients.
7. API Integration
SaaS services easily integrate with other software or services through standard APIs.
8. No client-side installation
SaaS services are accessed directly from the service provider using the internet connection, so
do not need to require any software installation.
Disadvantages of SaaS cloud computing layer
1) Security
Actually, data is stored in the cloud, so security may be an issue for some users. However,
cloud computing is not more secure than in-house deployment.
2) Latency issue
Since data and applications are stored in the cloud at a variable distance from the end-user,
there is a possibility that there may be greater latency when interacting with the application
compared to local deployment. Therefore, the SaaS model is not suitable for applications
whose demand response time is in milliseconds.
3) Total Dependency on Internet
Without an internet connection, most SaaS applications are not usable.
4) Switching between SaaS vendors is difficult
Switching SaaS vendors involves the difficult and slow task of transferring the very
large data files over the internet and then converting and importing them into another
SaaS also.
Popular SaaS Providers
Er.Binay Yadav Page 14
Cloud Computing -RJU
The below table shows some popular SaaS providers and services that are provided by them
Provider Services
Salseforce.com On-demand CRM solutions
Microsoft Office 365 Online office suite
Google Apps Gmail, Google Calendar, Docs, and sites
NetSuite ERP, accounting, order management, CRM, Professionals
Services Automation (PSA), and e-commerce applications.
GoToMeeting Online meeting and video-conferencing software
Constant Contact E-mail marketing, online survey, and event marketing
Oracle CRM CRM applications
Workday, Inc Human capital management, payroll, and financial
management.
Deployment models
Deployment models define the type of access to the cloud, i.e., how the cloud is located? Cloud
can have any of the four types of access: public, private, hybrid and community.
Public cloud:
The public cloud allows systems and services to be easily accessible to general public.
Amazon Elastic Compute Cloud (EC2), Microsoft Azure, IBM's Blue Cloud, Sun
Cloud, and Google Cloud are examples of the public cloud.
Er.Binay Yadav Page 15
Cloud Computing -RJU
Benefits
There are many benefits of deploying cloud as public cloud model. The following diagram
shows some of those benefits:
Cost effective
Since public cloud share same resources with large number of consumer, it has low cost.
Reliability
Since public cloud employs large number of resources from different locations, if any of the
resource fail, public cloud can employ another one.
Flexibility
It is also very easy to integrate public cloud with private cloud, hence gives consumers a
flexible approach.
Location independence
Since, public cloud services are delivered through internet, therefore ensures location
independence.
Utility style costing
Public cloud is also based on pay-per-use model and resources are accessible whenever
consumer needs it.
High scalability
Cloud resources are made available on demand from a pool of resources, i.e., they can be
scaled up or down according the requirement.
Disadvantages
Here are the disadvantages of public cloud model:
Low security
In public cloud model, data is hosted off-site and resources are shared publicly, therefore
does not ensure higher level of security.
Less customizable
It is comparatively less customizable than private cloud.
Private cloud:
The private cloud allows systems and services to be accessible within an organization. The
private cloud is operated only within a single organization. However, it may be managed
internally or by third-party. The chief advantage of these systems is that the enterprise
retains full control
Over corporate data, security guidelines, and system performance.
Benefits
There are many benefits of deploying cloud as private cloud model. The following diagram
shows some of those benefits:
Higher security and privacy
Private cloud operations are not available to general public and resources are shared from
distinct pool of resources, therefore, ensures high security and privacy.
More control
Er.Binay Yadav Page 16
Cloud Computing -RJU
Private clouds have more control on its resources and hardware than public cloud because it
is accessed only within an organization.
Cost and energy efficiency
Private cloud resources are not as cost effective as public clouds but they offer more
efficiency than public cloud.
Disadvantages
Here are the disadvantages of using private cloud model:
Restricted area
Private cloud is only accessible locally and is very difficult to deploy globally.
Inflexible pricing
In order to fulfill demand, purchasing new hardware is very costly.
Limited scalability
Private cloud can be scaled only within capacity of internal hosted resources.
Additional skills
In order to maintain cloud deployment, organization requires more skilled and expertise.
Hybrid cloud:
This can be a combination of private and public clouds that support the requirement to retain
some data in an organization, and also the need to offer services in the cloud. A company
may use internal resources in a private cloud and maintain total control over its proprietary
data. It can then use a public cloud storage provider for backing up less sensitive
information.
Benefits
There are many benefits of deploying cloud as hybrid cloud model. The following diagram
shows some of those benefits:
Scalability
It offers both features of public cloud scalability and private cloud scalability.
Er.Binay Yadav Page 17
Cloud Computing -RJU
Flexibility
It offers both secure resources and scalable public resources.
Cost efficiencies
Public cloud are more cost effective than private, therefore hybrid cloud can have this saving.
Security
Private cloud in hybrid cloud ensures higher degree of security.
Disadvantage
s Networking
issues
Networking becomes complex due to presence of private and public cloud.
Security compliance
It is necessary to ensure that cloud services are compliant with organization's security policies.
Infrastructural dependency
The hybrid cloud model is dependent on internal it infrastructure, therefore it is necessary
to ensure redundancy across data centers.
Community cloud:
The community cloud allows system and services to be accessible by group of
organizations. It shares the infrastructure between several organizations from a specific
community. It may be managed internally or by the third-party.
Benefits
There are many benefits of deploying cloud as community cloud model. The following
diagram shows some of those benefits:
Cost effective
Community cloud offers same advantage as that of public\ cloud at low cost. Sharing
between organizations community cloud provides an infrastructure to share cloud resources
and capabilities among several organizations.
Security
Community cloud is comparatively more secure than the public cloud.
Er.Binay Yadav Page 18
Cloud Computing -RJU
Issues
since all data is housed at one location, one must be careful in storing data in community
cloud because it might be accessible by others.
It is also challenging to allocate responsibilities of governance, security and cost.
It
Service Oriented Architecture (SOA)
A Service-Oriented Architecture or SOA is a design pattern which is designed to build
distributed systems that deliver services to other applications through the protocol. It is
only a concept and not limited to any programming language or platform.
Service
A service is a well-defined, self-contained function that represents a unit of functionality. A
service can exchange information from another service. It is not dependent on the state of
another service. It uses a loosely coupled, message-based communication model to
communicate with applications and other services.
Service Connections
The figure given below illustrates the service-oriented architecture. Service consumer sends
a service request to the service provider, and the service provider sends the service response
to the service consumer. The service connection is understandable to both the service
consumer and service provider.
Service-Oriented Terminologies
Let's see some important service-oriented terminologies:
Er.Binay Yadav Page 19
Cloud Computing -RJU
o Services - The services are the logical entities defined by one or more
published interfaces.
o Service provider - It is a software entity that implements a service specification.
o Service consumer - It can be called as a requestor or client that calls a service
provider. A service consumer can be another service or an end-user application.
o Service locator - It is a service provider that acts as a registry. It is
responsible for examining service provider interfaces and service locations.
o Service broker - It is a service provider that pass service requests to one or
more additional service providers.
Characteristics of SOA
The services have the following characteristics:
o They are loosely coupled.
o They support interoperability.
o They are location-transparent
o They are self-contained.
Components of service-oriented architecture
The service-oriented architecture stack can be categorized into two parts - functional aspects
and quality of service aspects.
Er.Binay Yadav Page 20
Cloud Computing -RJU
Functional aspects
The functional aspect contains:
o Transport - It transports the service requests from the service consumer to the
service provider and service responses from the service provider to the service
consumer.
o Service Communication Protocol - It allows the service provider and the
service consumer to communicate with each other.
o Service Description - It describes the service and data required to invoke it.
o Service - It is an actual service.
o Business Process - It represents the group of services called in a particular
sequence associated with the particular rules to meet the business requirements.
o Service Registry - It contains the description of data which is used by service
providers to publish their services.
Quality of Service aspects
The quality-of-service aspects contains:
o Policy - It represents the set of protocols according to which a service provider
makes and provide the services to consumers.
o Security - It represents the set of protocols required for identification and
authorization.
o Transaction - It provides the surety of consistent result. This means, if we use the
group of services to complete a business function, either all must complete or none
of the complete.
o Management - It defines the set of attributes used to manage the services.
Advantages of SOA
SOA has the following advantages:
o Easy to integrate - In a service-oriented architecture, the integration is a
service specification that provides implementation transparency.
o Manage Complexity - Due to service specification, the complexities get
isolated, and integration becomes more manageable.
o Platform Independence - The services are platform-independent as
they can communicate with other applications through a common
language.
o Loose coupling - It facilitates to implement services without impacting other
applications or services.
o Parallel Development - As SOA follows layer-based architecture, it provides
Er.Binay Yadav Page 21
Cloud Computing -RJU
parallel development.
o Available - The SOA services are easily available to any requester.
o Reliable - As services are small in size, it is easier to test and debug them.
Practical applications of SOA:
SOA is used in many ways around us whether it is mentioned or not.
1. SOA infrastructure is used by many armies and air force to deploy
situational awareness systems.
2. SOA is used to improve the healthcare delivery.
3. Nowadays many apps are games and they use inbuilt functions to run. For
example, an app might need GPS so it uses inbuilt GPS functions of the device.
This is SOA in mobile solutions.
4. SOA helps maintain museums a virtualized storage pool for their information
and content.
Er.Binay Yadav Page 22
You might also like
- ARCHIVE - Architecting For The Cloud - AWS Best Practices - AWS - Cloud - Best - PracticesNo ratings yetARCHIVE - Architecting For The Cloud - AWS Best Practices - AWS - Cloud - Best - Practices50 pages
- AWS Data Analytics Specialty Exam Cram NotesNo ratings yetAWS Data Analytics Specialty Exam Cram Notes43 pages
- IFS-annual Report 2022 Final 23-05-2023No ratings yetIFS-annual Report 2022 Final 23-05-202318 pages
- AWS Certified SysOps Administrator - Associate - AWS Certified SysOps Administrator - AssociateNo ratings yetAWS Certified SysOps Administrator - Associate - AWS Certified SysOps Administrator - Associate1 page
- AWS Certified Solutions Architect Associate Jon Bonso & Adrian Formaran All Chapters AvailableNo ratings yetAWS Certified Solutions Architect Associate Jon Bonso & Adrian Formaran All Chapters Available116 pages
- Case Study Based On: Cloud Deployment and Service Delivery ModelsNo ratings yetCase Study Based On: Cloud Deployment and Service Delivery Models10 pages
- Magic Quadrant For Enterprise File Synchronization and SharingNo ratings yetMagic Quadrant For Enterprise File Synchronization and Sharing40 pages
- A Micro-Service Strategy With Your Internal ServiceNow Instance - Architects - ServiceNow CommunityNo ratings yetA Micro-Service Strategy With Your Internal ServiceNow Instance - Architects - ServiceNow Community3 pages
- Central University of Haryana: Cloud Computing AssignmentNo ratings yetCentral University of Haryana: Cloud Computing Assignment9 pages
- Dot Net 9 Csharp 13 Features and Best PracticesNo ratings yetDot Net 9 Csharp 13 Features and Best Practices76 pages
- NetflixOSS - A Cloud Native Architecture - Slides PDFNo ratings yetNetflixOSS - A Cloud Native Architecture - Slides PDF86 pages
- N TierMulti-Tier 3-Tier 2-Tier Architecture With EXAMPLENo ratings yetN TierMulti-Tier 3-Tier 2-Tier Architecture With EXAMPLE7 pages
- A Survey On Security Issues in Service Delivery Models of Cloud ComputingNo ratings yetA Survey On Security Issues in Service Delivery Models of Cloud Computing11 pages
- Cloud Adoption Framework For Small and Medium-Size Enterprises SMEs in Ethiopia - Birhane WoldegebrealNo ratings yetCloud Adoption Framework For Small and Medium-Size Enterprises SMEs in Ethiopia - Birhane Woldegebreal108 pages
- WP RedisLabs Microservices Kubernetes 1560870546484No ratings yetWP RedisLabs Microservices Kubernetes 15608705464846 pages
- Simple Storage Service - S3: Ponnam Phani KrishnaNo ratings yetSimple Storage Service - S3: Ponnam Phani Krishna9 pages
- System Software Anna University Question Bank With KeyNo ratings yetSystem Software Anna University Question Bank With Key4 pages
- Getting Started With Windows Multi Point Mouse SDK100% (1)Getting Started With Windows Multi Point Mouse SDK15 pages
- MP Module 1 - The Intel Microprocessors 8086 Architecture - Aeraxia - In.No ratings yetMP Module 1 - The Intel Microprocessors 8086 Architecture - Aeraxia - In.16 pages
- Guide To SATA Hard Disks Installation and RAID ConfigurationNo ratings yetGuide To SATA Hard Disks Installation and RAID Configuration25 pages
- Microsoft Access 2010 Part 1: Introduction To Access: C S U, L ANo ratings yetMicrosoft Access 2010 Part 1: Introduction To Access: C S U, L A24 pages
- ENVY 14-3010NR Spectre: HP Is The World's Favorite PCNo ratings yetENVY 14-3010NR Spectre: HP Is The World's Favorite PC2 pages
- Oracle Solaris 10 Compared To Oracle Solaris 11No ratings yetOracle Solaris 10 Compared To Oracle Solaris 116 pages
- COA Lecture 18-Fully Associative, Set Associative PDFNo ratings yetCOA Lecture 18-Fully Associative, Set Associative PDF20 pages
- Voice Assistant Using Artificial Intelligence IJERTV11IS050242No ratings yetVoice Assistant Using Artificial Intelligence IJERTV11IS0502423 pages
- HikCentral Professional V1.6.0 - AE Specification - 20200302No ratings yetHikCentral Professional V1.6.0 - AE Specification - 20200302146 pages
- WPC All: WPC Oversh Ooting (Overla P With WPC Kpi)No ratings yetWPC All: WPC Oversh Ooting (Overla P With WPC Kpi)75 pages