0% found this document useful (0 votes)
1K views28 pagesChapter 1 Introduction To Electrical System
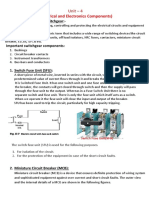
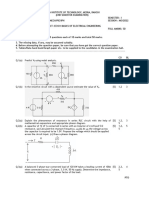
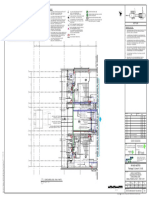
This chapter introduces the key elements of an electrical system including generation, transmission, distribution, and loads. It discusses the four major components: generation from various sources, transmission through power lines, distribution through local networks, and loads from consumers. A brief history of electrical systems is provided from early long-distance transmission in the 1890s to modern utility regulation. An overview of the Malaysian electrical grid operated by TNB, SESB, and SEB is also presented.
Uploaded by
visaggan sivabalanCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd
0% found this document useful (0 votes)
1K views28 pagesChapter 1 Introduction To Electrical System
This chapter introduces the key elements of an electrical system including generation, transmission, distribution, and loads. It discusses the four major components: generation from various sources, transmission through power lines, distribution through local networks, and loads from consumers. A brief history of electrical systems is provided from early long-distance transmission in the 1890s to modern utility regulation. An overview of the Malaysian electrical grid operated by TNB, SESB, and SEB is also presented.
Uploaded by
visaggan sivabalanCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd
/ 28