0% found this document useful (0 votes)
128 views26 pagesPhysics Exercise 5
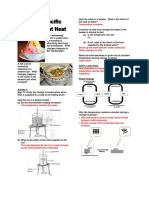
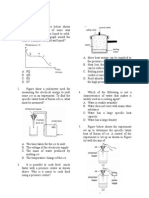
This document contains a 30 question multiple choice exercise about heat, gases, and the process of changing state from solid to liquid to gas. It provides definitions and values for the specific heat of fusion and vaporization of ice and water, and questions assess understanding of concepts like internal energy change during phase changes, molecular kinetic and potential energy, cooling and heating curves, and calculating energy and time required for different processes.
Uploaded by
Law Jing SeeCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd
0% found this document useful (0 votes)
128 views26 pagesPhysics Exercise 5
This document contains a 30 question multiple choice exercise about heat, gases, and the process of changing state from solid to liquid to gas. It provides definitions and values for the specific heat of fusion and vaporization of ice and water, and questions assess understanding of concepts like internal energy change during phase changes, molecular kinetic and potential energy, cooling and heating curves, and calculating energy and time required for different processes.
Uploaded by
Law Jing SeeCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd
/ 26